Introduction to VMware
VMware is a global leader in cloud computing and virtualization technology, providing solutions that revolutionize how businesses manage their IT infrastructure. VMware enables organizations to create, deploy, and manage virtual machines (VMs), improving flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
With VMware, companies can reduce their reliance on physical hardware, transitioning to software-defined environments that make IT operations more agile and responsive to changing needs. From data centers and hybrid clouds to desktop virtualization, VMware has become a cornerstone of modern IT solutions. This guide will explore VMware’s technology, the industries it serves, and the benefits it offers to businesses worldwide.
What Is VMware? An Overview of Virtualization Technology

VMware is a leading provider of virtualization software, which allows users to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical computer. In simple terms, virtualization means creating a virtual version of something—like an operating system, server, or storage device—rather than relying on dedicated hardware. VMware’s software solutions are designed to abstract and pool resources, such as CPUs, memory, and storage, allowing organizations to run several applications and services on fewer physical machines.
One of the company’s flagship products is VMware vSphere, a comprehensive virtualization platform used by enterprises to manage large-scale virtualized environments. Other products like VMware Workstation and VMware Fusion allow individuals to run multiple operating systems (like Windows and Linux) on personal computers. VMware’s virtualization technology plays a critical role in optimizing data center operations, enabling cloud deployments, and supporting remote work environments through tools like VMware Horizon.
What Is VMware and What Does It Do?
VMware provides a variety of solutions aimed at modernizing IT infrastructure, managing hybrid cloud environments, and securing applications. Its core technology revolves around virtualization, which separates computing resources from the underlying hardware to create flexible and scalable environments. With VMware, organizations can easily create, deploy, and manage virtual machines across multiple data centers and cloud platforms.
What Industry Is VMware In?
VMware operates in the technology and software industry, specifically focusing on cloud computing, virtualization, and digital infrastructure management. The company’s solutions are essential in several sectors, including enterprise IT, telecommunications, healthcare, education, retail, finance, and government services. As a pioneer in virtualization, VMware has expanded beyond traditional IT infrastructure to offer software for hybrid cloud management, container orchestration, and cybersecurity.
Why Should You Use VMware? Key Benefits Explained

VMware offers numerous benefits that make it a preferred choice for businesses and IT professionals. One of the primary advantages of VMware is resource optimization. By virtualizing servers and storage, organizations can run multiple applications on a single machine, reducing hardware costs and improving server utilization. This results in significant savings on capital expenses (CapEx) and operating expenses (OpEx), as companies can reduce power consumption, cooling costs, and physical space requirements.
VMware Products and Solutions
VMware offers a diverse range of products and solutions that empower businesses to virtualize their infrastructure, manage hybrid cloud environments, and secure endpoints. These products cover desktop virtualization, data center management, networking, security, and cloud platforms, providing flexible solutions for enterprises of all sizes. Below is an overview of some of VMware’s key products and their benefits.
What Is VMware Workstation, and Why Would You Want One?
VMware Workstation is a powerful virtualization tool that allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single desktop or laptop. It is popular among developers, IT professionals, and testers who need to simulate different environments without the need for physical hardware. With features like seamless integration, drag-and-drop file sharing, and the ability to run complex networks on a single machine, VMware Workstation provides a robust platform for testing, coding, and learning. Additionally, it supports snapshots, enabling users to revert to a previous state, which is ideal for software testing and troubleshooting.
What Is VMware Horizon?
VMware Horizon is a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solution that delivers secure, remote access to desktops and applications. It enables organizations to host desktops centrally in data centers or the cloud and stream them to users on-demand. Horizon supports hybrid environments, ensuring users can access their virtual workspace from any device or location, improving workforce flexibility. It also integrates with other VMware products like Workspace ONE and NSX, offering advanced security and endpoint management features.
What Is VMware Horizon Client?
The VMware Horizon Client is the end-user software that connects users to their virtual desktops hosted on the Horizon platform. It is available on various devices, including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android, allowing employees to access their work environment remotely. The Horizon Client ensures high-performance connectivity with features like adaptive bandwidth usage and optimized display protocols, providing a seamless experience even on low-speed networks.
What Is VMware Horizon View?
VMware Horizon View is a component of the Horizon platform that focuses on managing and delivering virtual desktops. It streamlines the deployment and administration of thousands of virtual desktops with features like desktop pools and automated provisioning. Horizon View offers advanced capabilities like load balancing and remote monitoring, making it ideal for large enterprises with a distributed workforce.
What Is VMware Horizon View Client?
The VMware Horizon View Client is a lightweight application that allows end-users to connect to Horizon View virtual desktops. It offers secure access with multi-factor authentication and ensures a consistent user experience across devices. With features like persistent desktops and real-time collaboration tools, the Horizon View Client enhances productivity for remote teams.
What Is VMware Fusion? A Deep Dive into Mac Virtualization
VMware Fusion is a virtualization software designed specifically for macOS users, allowing them to run Windows, Linux, or other operating systems alongside macOS. It offers seamless integration with macOS features like drag-and-drop and copy-paste between virtual machines and the host OS. VMware Fusion is widely used by developers who need to test cross-platform software and by business users who require access to Windows-only applications on their Mac devices.
What Is VMware Fusion Pro? Features and Use Cases
VMware Fusion Pro is an advanced version of Fusion, targeted at power users and IT professionals. It offers features like linked clones, snapshots, and enhanced network configurations, making it suitable for complex development and testing environments. Fusion Pro supports REST APIs, enabling automation workflows and integration with other tools. It is ideal for organizations that need to deploy and manage multiple virtual machines efficiently on macOS.
What Is VMware Cloud Foundation?
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) is an integrated platform that combines compute, storage, networking, and cloud management. It provides a consistent infrastructure for managing both private and hybrid cloud environments, making it easier to deploy and operate multi-cloud solutions. VCF integrates with VMware’s NSX, vSphere, and vSAN, providing a comprehensive software-defined data center (SDDC) architecture. It simplifies operations through automation, allowing enterprises to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure management.
What Is VMware NSX? Overview of Network Virtualization
VMware NSX is a network virtualization platform that provides advanced networking and security services. It abstracts networking functionality from the underlying hardware, allowing businesses to create, manage, and secure their networks programmatically. NSX supports micro-segmentation, which isolates workloads to prevent lateral movement of threats, enhancing security. It also integrates with public cloud providers like AWS and Azure, making it a key component in hybrid cloud strategies.
What Is VMware Tanzu? Kubernetes and Cloud-Native Applications
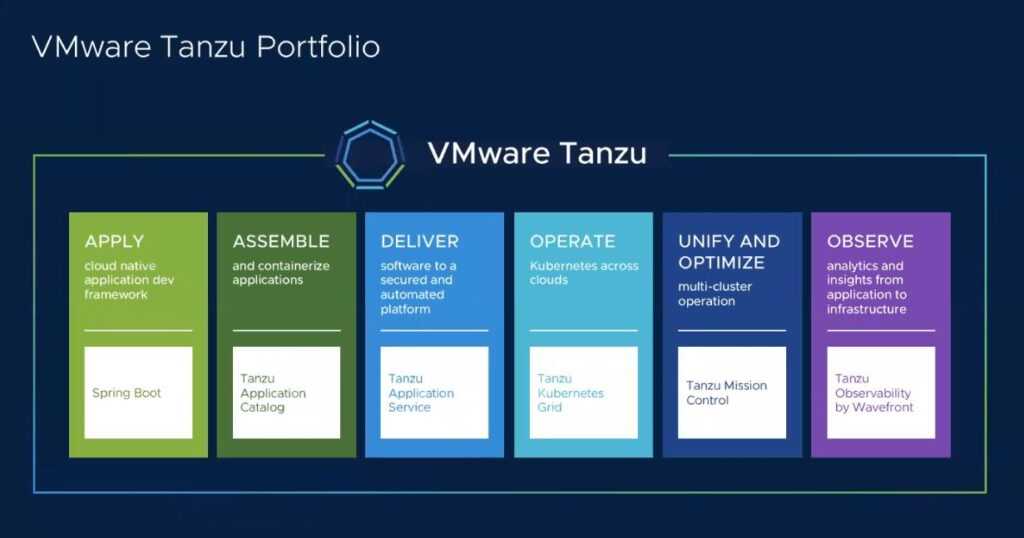
VMware Tanzu is a suite of products focused on modern application development using containers and Kubernetes. It enables enterprises to build, manage, and scale cloud-native applications across multi-cloud environments. Tanzu simplifies the management of Kubernetes clusters, provides observability into application performance, and supports DevOps practices by integrating with CI/CD pipelines. With Tanzu, organizations can accelerate their digital transformation by delivering applications faster and more reliably.
What Is VMware Carbon Black? Security and Threat Detection
VMware Carbon Black is a next-generation security platform that focuses on endpoint detection and response (EDR). It provides real-time threat detection, behavioral analysis, and automated response capabilities. Carbon Black is designed to combat advanced threats, such as ransomware and fileless malware, by continuously monitoring endpoints and using artificial intelligence to detect anomalies. It integrates with other VMware tools, offering a unified approach to security across virtual and cloud environments.
What Is VMware Workspace ONE? A Guide to Endpoint Management
VMware Workspace ONE is a digital workspace platform that provides unified endpoint management (UEM) for desktops, mobile devices, and IoT endpoints. It allows IT administrators to manage and secure devices from a single console while ensuring users have access to the apps and resources they need. Workspace ONE supports identity-based access controls and integrates with Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, and other SaaS applications, offering a seamless experience for end-users. It also provides analytics to monitor device health and ensure compliance with corporate policies.
What Is VMware Cloud? Solutions for Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
VMware Cloud is a suite of services that enables businesses to run, manage, and secure applications across public, private, and hybrid cloud environments. It supports multi-cloud strategies by providing consistent infrastructure and operations across cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. VMware Cloud simplifies workload migration, reduces operational complexity, and ensures security compliance across environments. Its integrated tools allow businesses to leverage the scalability of public clouds while retaining control over sensitive data.
What Is VMware Aria?
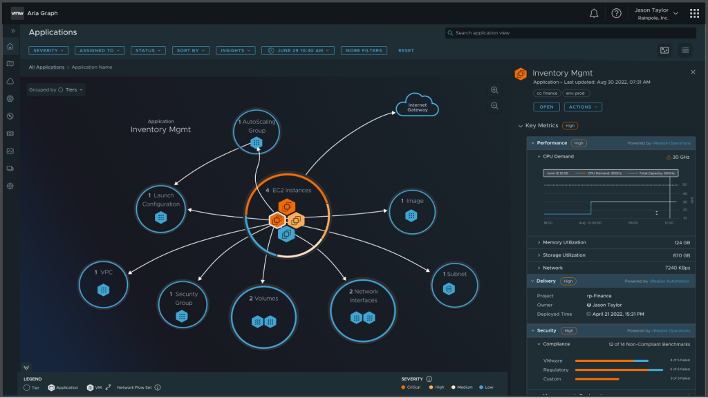
VMware Aria is a multi-cloud management platform designed to provide visibility, control, and optimization for cloud environments. It helps enterprises monitor cloud usage, manage costs, and ensure compliance across multiple cloud providers. VMware Aria offers advanced analytics to predict resource consumption and automate workload management, enabling organizations to optimize their cloud spending. With Aria, businesses can gain deeper insights into their cloud operations and make data-driven decisions for improved efficiency.
VMware Hypervisors and Platforms
VMware is at the forefront of virtualization technology, offering a robust ecosystem that enables organizations to optimize IT operations. Its core products, including VMware ESXi, vSphere, vCenter, DRS, vSAN, and NSX, power virtualized infrastructure solutions across industries. Below, we explore these platforms in detail, focusing on their architecture, features, and benefits.
What Is VMware ESXi? Overview of VMware’s Bare-Metal Hypervisor
VMware ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor that allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server by abstracting hardware resources and allocating them efficiently. As the foundation of VMware’s virtualization platform, ESXi provides a lightweight and robust architecture with a small footprint, enhancing performance and reliability.
What Is VMware vSphere? Architecture and Features Explained
VMware vSphere is a comprehensive virtualization platform that combines ESXi hypervisors and vCenter Server for centralized management. It forms the backbone of most virtualized environments by creating a software-defined data center (SDDC). With vSphere, organizations can optimize resource allocation across multiple servers and run applications with high availability.
The architecture of vSphere consists of two main components: ESXi hosts that handle the virtualization layer and vCenter Server, which provides centralized control. Features such as Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), vMotion, and vSAN are seamlessly integrated, making vSphere a powerful tool for automating workloads, balancing resources, and minimizing downtime.
What Is vCenter in VMware? Managing Virtualized Environments
vCenter Server is the centralized management platform for VMware vSphere environments, enabling IT administrators to manage multiple ESXi hosts and VMs from a single interface. With vCenter, users can monitor performance, allocate resources, and automate routine tasks.
Key functionalities include template-based provisioning, snapshot management, and resource pools that optimize the distribution of CPU, memory, and storage resources. Through the vCenter dashboard, administrators can perform operations like live VM migrations (vMotion), monitor resource utilization, and configure disaster recovery solutions.
What Is VMware DRS? Dynamic Resource Scheduling in VMware
VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) is a critical feature of vSphere that ensures workloads run efficiently by dynamically balancing resources across multiple ESXi hosts. It automates the process of assigning CPU and memory resources to virtual machines, ensuring consistent performance even under fluctuating loads.
DRS continuously monitors the resource usage of VMs and adjusts their placement or resource allocation in real time. For instance, if a host becomes overutilized, DRS can migrate VMs to another host using vMotion, ensuring that workloads remain balanced. This capability minimizes performance bottlenecks and ensures optimal uptime without manual intervention.
What Is VMware vSAN? Virtual SAN and Storage Solutions
VMware vSAN (Virtual SAN) is an enterprise-grade, hyper-converged storage solution integrated directly with the vSphere platform. It aggregates local and networked storage from multiple ESXi hosts to create a shared datastore, eliminating the need for traditional storage arrays.
vSAN provides seamless storage management for virtual machines, supporting policy-driven provisioning to ensure data availability and performance. Organizations benefit from high availability, as vSAN automatically distributes data across multiple hosts, ensuring that workloads remain available even if a host fails.
What Is NSX in VMware? Advanced Networking Concepts
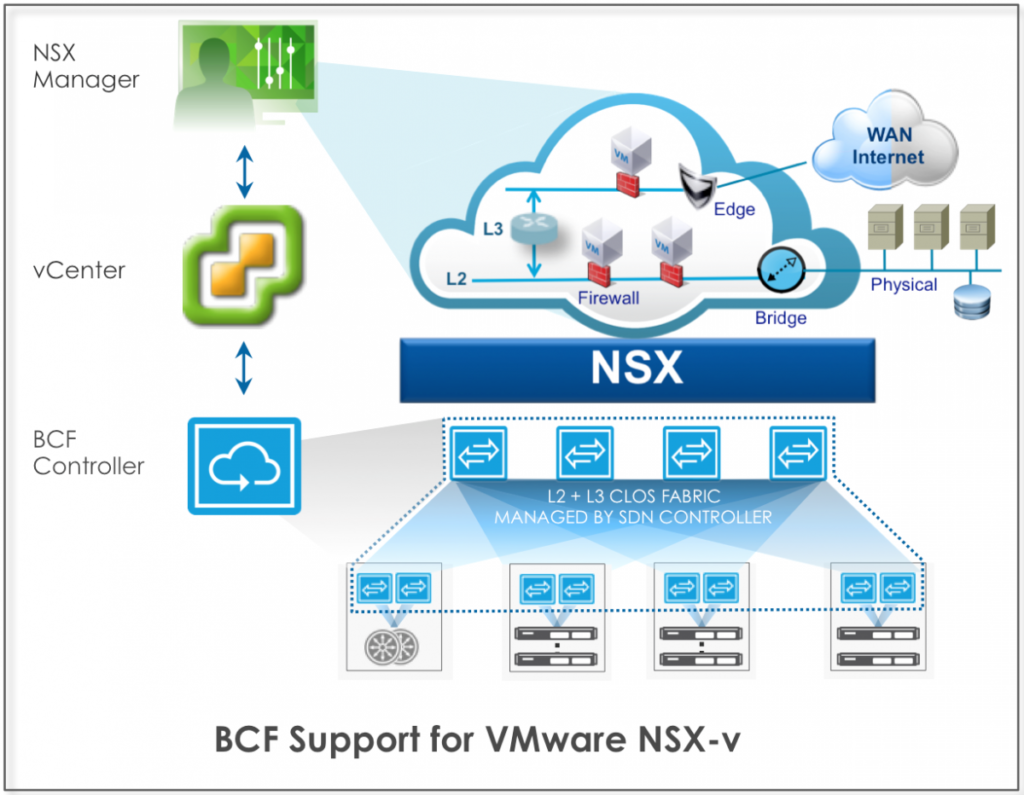
VMware NSX is a network virtualization platform that enables software-defined networking (SDN). NSX abstracts networking functions from the underlying hardware, allowing organizations to create, configure, and manage networks entirely in software. This level of abstraction increases flexibility, as network services like firewalls, load balancers, and VPNs can be deployed or adjusted without reconfiguring physical infrastructure.
With NSX, IT teams can implement micro-segmentation, which isolates workloads at a granular level, improving security by limiting the spread of potential threats. Automation capabilities further streamline network management, as NSX integrates with vSphere and third-party solutions to support multi-cloud environments.
VMware Tools and Utilities
In the world of virtualization, VMware tools and utilities play a critical role in optimizing virtual machine (VM) performance, enhancing user experience, and simplifying infrastructure management. These solutions encompass a wide variety of tools that cater to different aspects of virtual environments—ranging from performance tuning and data recovery to seamless migration tools and software utilities. Below, we dive deep into some of the most significant VMware tools and how they contribute to a robust virtualization ecosystem.
What Is VMware Tools? Importance and How to Use It
VMware Tools is a suite of utilities designed to enhance the performance and manageability of virtual machines running on VMware hypervisors, including VMware Workstation, ESXi, and Fusion. Once installed on a VM, it ensures better integration between the host system and the guest operating system. This tool improves features like mouse synchronization, time synchronization, and the ability to copy and paste between the host and guest systems.
What Is VMware HCX? Simplifying Cloud Migrations
VMware HCX (Hybrid Cloud Extension) is a cloud migration tool that simplifies moving workloads between different data centers or between on-premises and cloud environments. It is particularly useful for organizations aiming to modernize their infrastructure by adopting hybrid or multi-cloud strategies.
What Is VMware Data Recovery? Backup and Disaster Recovery Solutions
VMware Data Recovery (VDR) is a built-in backup and recovery solution specifically designed to work with VMware environments. It ensures efficient backup of virtual machines by utilizing technologies like changed block tracking (CBT), which reduces the amount of data processed during backups. VDR is particularly effective for organizations that rely on virtual infrastructure for critical applications, providing peace of mind in case of unexpected failures or data corruption.
What Is Enhanced Keyboard Driver VMware? A Guide to Keyboard Functionality
The VMware Enhanced Keyboard Driver is a utility designed to improve the keyboard functionality of virtual machines. It becomes essential in situations where the default keyboard drivers fail to work properly inside guest operating systems, such as during OS installation or when accessing recovery modes. This tool ensures that all keyboard keys, including special keys and hotkeys, function as expected inside the VM.
What Is the VMware Enhanced Keyboard Driver Used For?
The VMware Enhanced Keyboard Driver improves the user experience by addressing input-related issues inside virtual machines, especially during critical operations. For instance, when setting up a new guest OS, the absence of proper drivers might lead to malfunctioning keyboard inputs. The enhanced driver ensures consistent performance by making it possible to use all keys and shortcuts in situations where standard drivers don’t suffice.
What Is VMware vMotion? Migrating Virtual Machines in Real-Time
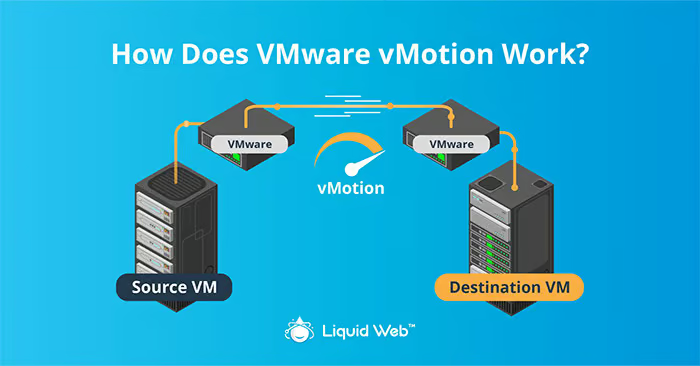
VMware vMotion is a powerful technology that enables the live migration of virtual machines between ESXi hosts without disrupting their services. It allows administrators to move running VMs from one host to another in real time, maintaining application uptime and ensuring seamless performance for end-users.
What Is VMware Player? A Free Virtualization Tool for Users
VMware Player, now known as VMware Workstation Player, is a lightweight virtualization solution designed for individuals and small businesses. It allows users to run multiple operating systems as virtual machines on a single host machine, making it an excellent tool for testing software, learning new operating systems, or creating isolated environments.
Technical Components and Features in VMware
VMware provides a vast array of technologies and components that enable efficient virtualization and cloud computing. Understanding these technical elements helps businesses and IT administrators optimize their infrastructure. This section explains crucial components and features in VMware, including clusters, datastores, connection servers, and distributed switches, among others. These elements play a pivotal role in network, storage, and virtual machine (VM) management, ensuring scalability, security, and seamless resource allocation.
What Is a Cluster in VMware? Overview and Use Cases
A cluster in VMware is a logical grouping of multiple ESXi hosts that share resources like CPU, memory, and storage to act as a single computing entity. Clustering provides load balancing, fault tolerance, and resource management. With VMware DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler), workloads are automatically shifted between hosts to ensure optimal performance. If one host fails, HA (High Availability) restarts the virtual machines on other functioning hosts in the cluster.
What Is a Connection Server in VMware?
A Connection Server in VMware Horizon is the central management hub responsible for authentication and connection brokering between end users and virtual desktops or published applications. It manages user requests and provides seamless access to virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) sessions. The connection server ensures that users are directed to the right virtual machine or published app based on predefined policies.
What Is a Datastore in VMware? Storage Management Explained
A datastore in VMware refers to a logical storage container where virtual machine files and other resources are stored. It abstracts the underlying physical storage, whether it’s a local disk, SAN (Storage Area Network), or NAS (Network-Attached Storage). Datastores use VMFS (Virtual Machine File System), an optimized file system designed for virtual machines, enabling multiple VMs to access shared storage concurrently.
What Is a Distributed Switch in VMware? Networking Concepts
A distributed switch (vDS) in VMware allows centralized management of network configurations across multiple ESXi hosts. Unlike standard virtual switches, which need to be configured on each host individually, a distributed switch offers a centralized platform for setting up virtual networks and policies. This ensures consistency and reduces administrative overhead.
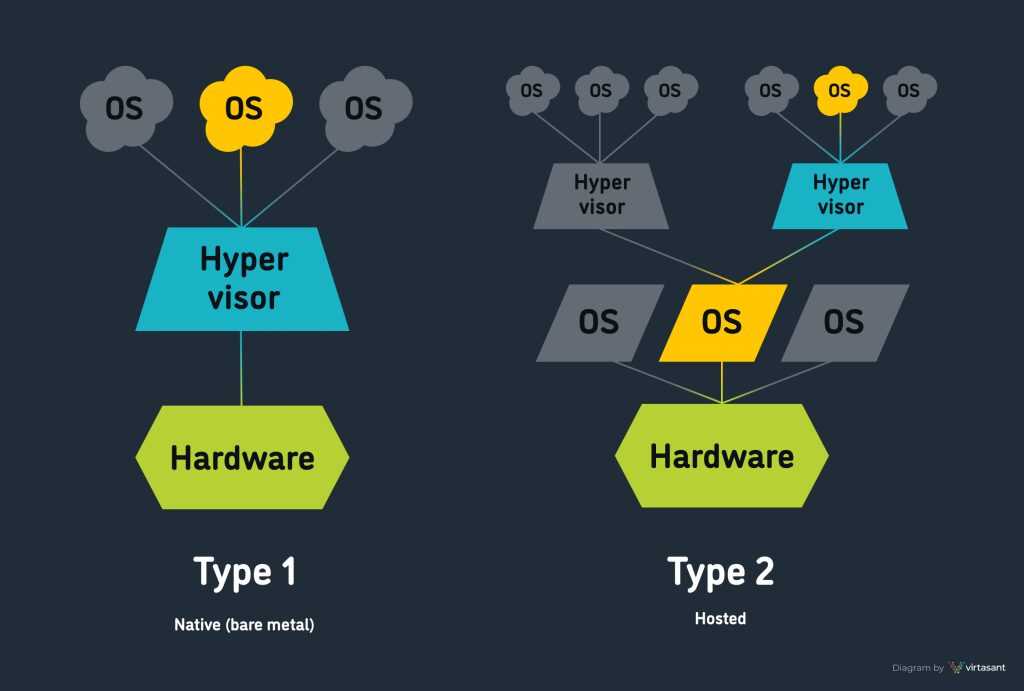
What Is a Hypervisor in VMware? Virtualization Explained
A hypervisor is the core technology that makes virtualization possible by allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server. VMware uses two types of hypervisors:
- ESXi (bare-metal hypervisor): Runs directly on physical hardware and is known for its high performance and low overhead.
- VMware Workstation and Fusion (hosted hypervisors): Run on top of an existing operating system, enabling users to create and run virtual machines on their desktop or laptop.
Hypervisors help organizations maximize resource utilization, isolate workloads, and run multiple operating systems on the same hardware, reducing costs and increasing flexibility.
What Is a LUN in VMware?
A LUN (Logical Unit Number) is a logical representation of a physical storage device presented to an ESXi host. LUNs are commonly used in SAN (Storage Area Networks) and are essential for provisioning storage to virtual machines.
What Is a Port Group in VMware? How It Works in Networking
A port group in VMware is a logical grouping of ports on a virtual switch. It defines network policies such as VLAN settings, traffic shaping, and security rules. Each port group is associated with a specific network segment, ensuring isolated traffic flows for different VMs.
What Is a Snapshot in VMware? Use Cases and Best Practices
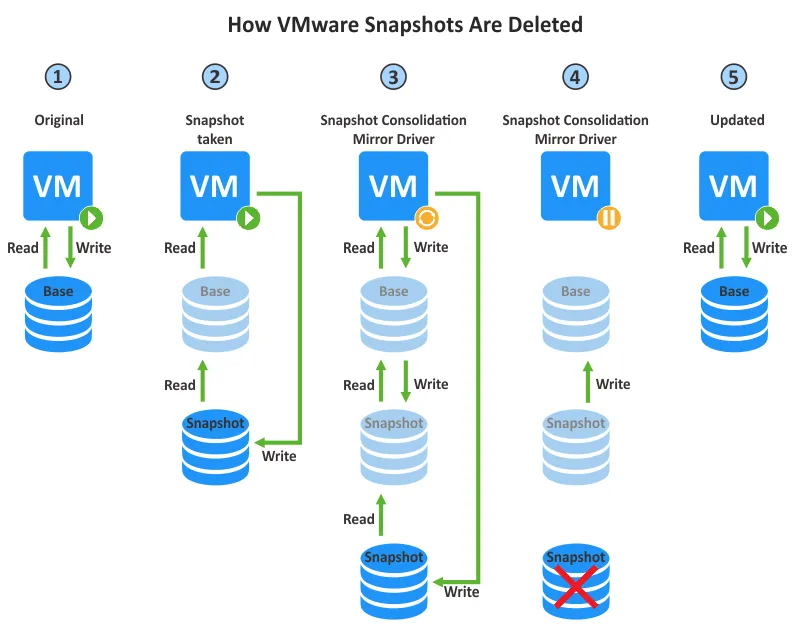
A snapshot in VMware captures the state, configuration, and data of a virtual machine at a specific point in time. It’s used for backup purposes or when testing changes, allowing administrators to revert to a previous state if needed. Snapshots save the VM’s disk, memory, and power state.
What Is a Template in VMware? Simplifying VM Deployment
A template in VMware is a golden image of a virtual machine that serves as the basis for creating multiple identical VMs. It contains the operating system, applications, and configurations, ensuring that new VMs are deployed consistently and efficiently.
What Is a VIB in VMware? VMware Installation Bundles Explained
A VIB (VMware Installation Bundle) is a software package that contains drivers, patches, and modules used to extend the functionality of VMware ESXi hosts. VIBs can be installed, removed, or updated via the ESXi command line or vSphere client.
What Is VMware Appliance? Pre-Packaged Virtual Machines
A VMware appliance is a pre-configured virtual machine containing a specific operating system and software application. These appliances are distributed in OVA or OVF format and are ready to run upon deployment.
VMware appliances simplify the deployment of software applications, eliminating the need for manual installation and configuration. They are often used for testing, development, and rapid prototyping, as well as deploying firewalls, monitoring tools, and web servers.
File Formats and Data Management in VMware
VMware’s platform relies on various file formats and data structures that help manage virtual machines, configuration settings, and snapshots efficiently. Understanding these file formats is essential for IT administrators, as they ensure smooth operations, proper backups, and seamless migrations. Each file type plays a specific role in the virtualization ecosystem. Below, we’ll dive into the key VMware file formats, what they are used for, and their importance in managing virtual infrastructures.
What Is an OVA File in VMware?
An OVA (Open Virtual Appliance) file is a packaged format used by VMware and other virtualization platforms to distribute pre-configured virtual machines (VMs) or appliances. This format bundles all the essential VM files, such as the disk image (.vmdk), metadata, and configuration files (.ovf), into a single, portable package. The OVA format simplifies the deployment process by allowing users to quickly import a virtual machine into VMware environments without extensive manual configuration.
What Is a .lck File in VMware? Lock Files Explained
A .lck (lock) file is a temporary file created by VMware to ensure that only one instance of a virtual machine or file is active at a time. These files play a crucial role in preventing multiple processes from accessing the same virtual machine’s resources simultaneously, which could lead to data corruption or instability. VMware creates .lck files when a VM is running or in use, and they are automatically deleted when the VM shuts down or is powered off properly.
What Is a .mf File in VMware? File Structure Overview
The .mf (manifest) file is an integral part of the OVA and OVF package structure. It contains hash values (checksums) for each component of the virtual appliance, such as the disk image and configuration files. The primary purpose of the .mf file is to ensure the integrity of the virtual appliance by verifying that none of its components have been tampered with or corrupted during transfer.
What Is Bootbank in VMware?
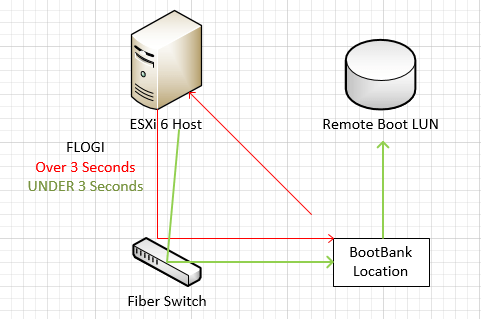
The bootbank in VMware refers to the area within ESXi hosts that stores important configuration files, firmware, and the hypervisor itself. VMware’s ESXi architecture divides the bootable storage into two partitions: primary and secondary bootbanks, providing redundancy in case one partition becomes corrupted. These bootbanks contain the startup binaries and system files required to initialize the hypervisor, making them essential for the stability of ESXi hosts.
What Format Is Used for VMware Images?
The .vmdk (Virtual Machine Disk) format is the primary file type used for storing virtual machine images in VMware environments. These files function as virtual hard disks, holding the guest operating system, applications, and user data within the VM. VMware supports several disk types—such as thin-provisioned, thick-provisioned, and split VMDKs—each offering different performance and storage benefits.
- Thin-provisioned VMDKs: Use only the space required by the data inside the VM, reducing storage waste.
- Thick-provisioned VMDKs: Pre-allocate the entire storage capacity to ensure better performance.
- Split VMDKs: Break large virtual disks into smaller chunks to improve backup and portability.
Performance Optimization and Resource Management
Performance optimization and resource management are critical components of VMware’s virtualization ecosystem. These processes ensure the efficient allocation and use of available system resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, across multiple virtual machines (VMs). VMware provides powerful tools and techniques, including ballooning, DRS, admission control, and affinity rules, to help administrators maintain performance, prevent resource contention, and optimize workloads. Proper resource management ensures that virtualized environments run smoothly without disruptions, minimizing downtime and enhancing system responsiveness. Below, we explore key aspects of VMware’s resource management features.
What Is Ballooning in VMware? Memory Management Techniques
Ballooning in VMware is a memory management technique that allows the hypervisor to reclaim memory from idle or underutilized VMs. When physical memory becomes scarce, the VMware ESXi hypervisor activates the balloon driver inside guest operating systems. This driver requests unused memory from the VM, simulating memory pressure. The reclaimed memory can then be allocated to other VMs that require it.
What Is Balloon Memory in VMware?
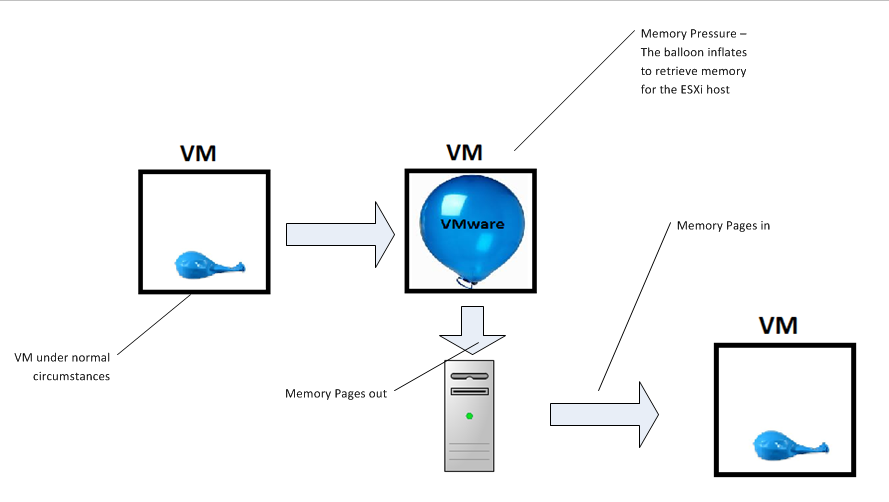
Balloon memory refers to the memory that is temporarily taken away from a guest VM by the ballooning process. The term describes how the balloon driver inflates by consuming a portion of the VM’s memory, thereby making it unavailable to the guest operating system. This “balloon” memory is handed back to the hypervisor, which redistributes it to other VMs.
What Is Acceptable Disk Latency in VMware?
Disk latency refers to the time it takes for an I/O operation (such as reading or writing data) to complete in a VMware environment. Acceptable disk latency depends on the workload, but a general benchmark is less than 20ms for read and write operations. Latency higher than this can indicate performance issues, often caused by storage contention, insufficient bandwidth, or misconfigurations.
What Is Admission Control in VMware?
Admission control is a feature in VMware that ensures a cluster always has enough resources available to accommodate the failover of virtual machines in case of a host failure. It prevents the overcommitment of resources by controlling how many VMs can be powered on based on the available resources in the cluster.
There are three primary policies for admission control:
- Host Failure Tolerance: Ensures that the cluster can withstand a predefined number of host failures.
- Resource Percentage: Reserves a certain percentage of CPU and memory resources in the cluster.
- Dedicated Host Failover: Keeps one or more hosts in reserve specifically for failover purposes.
By using admission control, VMware ensures high availability (HA) and helps avoid situations where there are insufficient resources to restart VMs during a host failure, improving system reliability.
What Is Affinity Rule in VMware? Optimizing VM Placement
Affinity rules in VMware control how virtual machines are placed across hosts within a cluster. These rules specify whether specific VMs should run together or be separated. An affinity rule ensures that certain VMs are kept on the same host, which is useful for workloads that need to communicate frequently and benefit from low-latency interactions.
There are two main types of affinity rules:
- VM-VM Affinity: Keeps two or more VMs on the same host.
- VM-Host Affinity: Ensures specific VMs are always assigned to certain hosts.
Administrators use affinity rules to optimize performance by reducing network traffic between VMs and ensuring workloads are hosted on optimal resources. However, excessive use of affinity rules can reduce the cluster’s flexibility, so they must be used judiciously.
What Are Affinity and Anti-Affinity Rules in VMware?
In addition to affinity rules, VMware provides anti-affinity rules, which ensure that specific VMs are kept on separate hosts. These rules are used to enhance availability and fault tolerance by preventing critical workloads from running on the same host.
What Is DRS in VMware? Resource Scheduling Overview
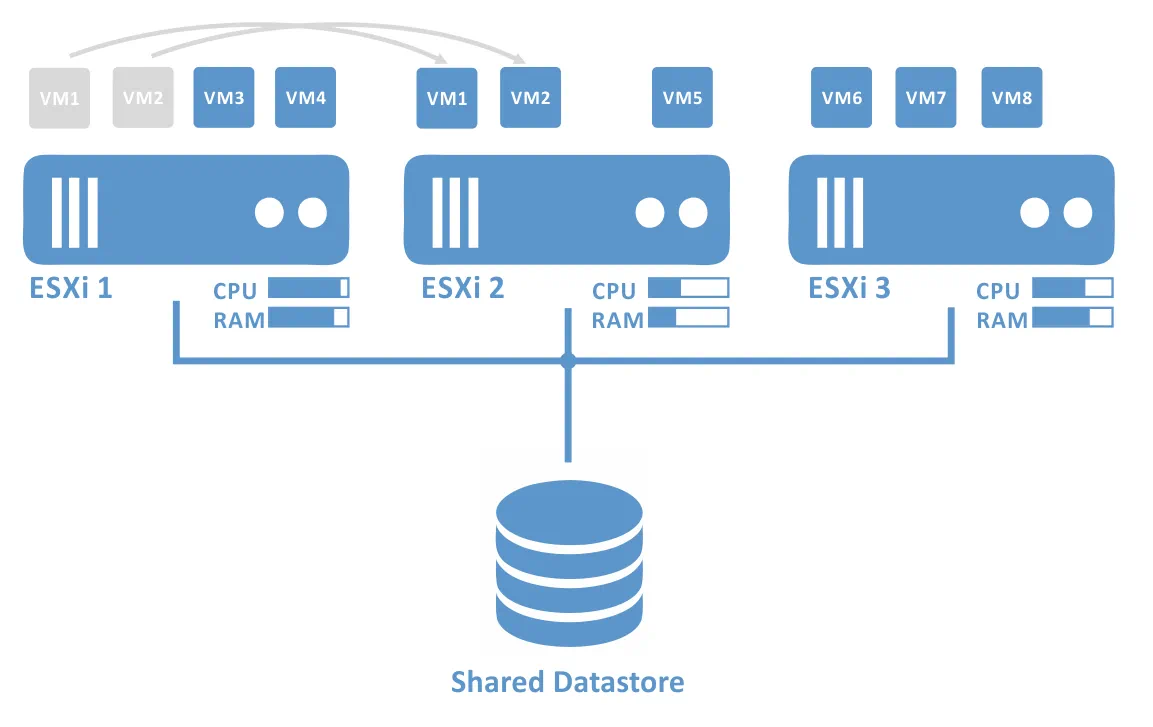
Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) in VMware is a tool that automates the load balancing of VMs across hosts within a cluster. DRS evaluates the CPU and memory usage of hosts and virtual machines in real-time. If it detects resource contention or an unbalanced workload, it recommends or automatically performs VM migrations using vMotion to optimize resource utilization.
DRS offers three operating modes:
- Manual Mode: Provides migration recommendations that administrators must approve.
- Partially Automated Mode: Automates initial placement but requires approval for subsequent migrations.
- Fully Automated Mode: Handles both placement and migrations without manual intervention.
By using DRS, organizations can maximize resource efficiency and maintain performance even as workloads change. It also improves fault tolerance, as VMs can be automatically migrated to healthy hosts when resources become constrained or a host experiences a failure.
Cloud Solutions and Hybrid Architectures
As organizations embrace digital transformation, cloud computing and hybrid architectures have become essential for maintaining operational agility and scalability. VMware offers a suite of solutions designed to simplify cloud adoption, enhance multi-cloud strategies, and bridge the gap between on-premises infrastructure and public cloud services. This section will provide an in-depth overview of key VMware cloud offerings, including Azure VMware Solution, VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF), and cloud automation capabilities, alongside a comparison of VMware and VirtualBox.
What Is the Azure VMware Solution?
The Azure VMware Solution (AVS) enables businesses to run VMware workloads natively on Microsoft Azure’s cloud infrastructure. This solution helps organizations seamlessly extend or migrate their on-premises VMware environments to the cloud without modifying applications or reconfiguring workloads. AVS supports popular VMware tools, including vSphere, vCenter, NSX-T, and vSAN, ensuring a familiar management experience.
Key features of AVS include:
- Disaster Recovery: Organizations can use AVS for backup and disaster recovery without building a new data center.
- Hybrid Cloud Model: Businesses can integrate their existing VMware workloads with Azure’s native cloud services, such as AI, analytics, and databases.
- Compliance and Security: AVS ensures compliance with various industry regulations, including GDPR and HIPAA, while using Azure’s built-in security framework.
This solution is particularly valuable for organizations looking to quickly migrate workloads to the cloud, implement a hybrid cloud strategy, or modernize legacy infrastructure.
What Is VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF)? Architecture Explained
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) is an integrated software platform that unifies compute, storage, networking, and cloud management into a single architecture. It provides a robust foundation for both private and hybrid clouds, enabling organizations to deploy and manage virtualized infrastructure with greater efficiency. VCF leverages core VMware technologies such as vSphere (compute virtualization), vSAN (storage virtualization), NSX-T (network virtualization), and vRealize Suite (cloud management).
The architecture of VCF includes:
- Management Domain: Used to deploy and manage the VMware environment, including vCenter and NSX Manager.
- Workload Domains: Each workload domain can support multiple clusters based on different workloads (e.g., VMs or Kubernetes clusters).
- Integrated Lifecycle Management: Automates patching and upgrades across the entire infrastructure.
VCF’s consistent infrastructure across private and public clouds allows businesses to scale workloads easily, adopt container-based applications, and ensure operational consistency.
What Is VMware VCF? A Complete Guide to Cloud Foundation
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) offers a comprehensive solution for building and managing hybrid cloud environments. This guide delves into the core components, use cases, and benefits of adopting VCF:
- Core Components: VCF integrates vSphere, NSX-T, vSAN, and the vRealize Suite to provide an end-to-end cloud infrastructure.
- Multi-Cloud Compatibility: VCF supports public cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, allowing seamless movement of workloads.
- Security and Compliance: Built-in tools for encryption, role-based access control, and compliance reporting make VCF a secure solution.
- Use Cases: Organizations leverage VCF for private cloud deployment, disaster recovery, and application modernization.
VCF simplifies cloud adoption by offering pre-configured software stacks and centralized management, reducing the operational complexity associated with multi-cloud strategies.
What Is VMware Cloud Automation?
VMware Cloud Automation enables businesses to streamline the deployment, management, and scaling of workloads across private, public, and hybrid cloud environments. Through tools like vRealize Automation and VMware Aria Automation, organizations can automate repetitive tasks, enforce governance policies, and improve resource utilization.
Key benefits of VMware Cloud Automation include:
- Automated Provisioning: Rapidly deploy virtual machines, containers, and applications with minimal manual intervention.
- Policy-Based Governance: Define and enforce security policies for workloads across multiple environments.
- Self-Service Cloud: Empower developers and end-users with on-demand access to IT resources via self-service portals.
- Cost Optimization: Track resource usage and optimize cloud spending using intelligent analytics.
This automation framework enables businesses to accelerate time-to-market, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the risk of human error.
VMware vs VirtualBox: Which Virtualization Software Is Better?
When choosing between VMware and VirtualBox, it’s essential to understand how these virtualization platforms differ in terms of features, performance, and use cases.
- VMware:
- Performance: VMware’s hypervisors (e.g., ESXi and Workstation) are optimized for high performance and scalability, making them ideal for enterprise environments.
- Features: VMware offers advanced features like vMotion, DRS, and vSAN, which are absent in VirtualBox.
- Use Cases: VMware is widely used in enterprise IT for production workloads, disaster recovery, and cloud integration.
- VirtualBox:
- Free and Open Source: VirtualBox is free to use and supports multiple host operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Ease of Use: It’s easier to set up, making it popular among individual users, developers, and educators.
- Limited Features: While sufficient for small-scale virtualization, it lacks the advanced features required for enterprise-level deployments.
Which Is Better?
If you’re a developer or student looking for a lightweight virtualization solution, VirtualBox might be sufficient. However, for businesses and enterprises seeking robust virtualization with advanced features, VMware is the superior option. VMware’s ability to integrate with cloud providers and manage large-scale environments makes it the better choice for production workloads and hybrid cloud deployments.
Security and Networking in VMware
Security and networking are critical aspects of VMware’s solutions, as virtualization environments require robust protection and seamless connectivity to ensure stability and efficiency. VMware offers a suite of technologies that cater to the specific needs of businesses, including network virtualization, threat prevention, and infrastructure management. In this section, we will explore VMware NSX, VMware Carbon Black, and the VMware CIM Server—three components that play pivotal roles in enhancing network security and performance within VMware environments.
What Is VMware NSX? Secure Network Virtualization
VMware NSX is a network virtualization platform that enables businesses to create and manage entire network infrastructures through software. Essentially, it abstracts the networking hardware into software components, allowing organizations to design, deploy, and manage virtual networks with the same flexibility they have with virtual machines (VMs). NSX empowers users to implement micro-segmentation, which ensures that individual workloads and VMs are isolated from each other, reducing the potential for lateral movement of cyber threats within the network.
One of the biggest advantages of VMware NSX is its ability to enable network automation and agility. Businesses can create dynamic network policies, automate network changes, and roll out new applications quickly without the constraints of physical infrastructure. NSX also integrates seamlessly with VMware vSphere environments, making it an essential tool for those leveraging VMware’s virtualization solutions. Additionally, NSX enhances security through distributed firewalls, load balancing, and VPN functionality, ensuring that networks remain protected against both internal and external threats.
What Is VMware Carbon Black? Threat Detection and Prevention
VMware Carbon Black is a next-generation endpoint protection platform designed to defend businesses against a wide range of security threats, including ransomware, malware, and fileless attacks. Acquired by VMware in 2019, Carbon Black focuses on endpoint and workload protection by continuously monitoring behaviors and patterns across devices and virtual machines. The platform provides real-time threat detection and response, enabling security teams to identify attacks as they happen and respond swiftly to mitigate potential damage.
What Is VMware CIM Server? Management Integration
The VMware CIM (Common Information Model) Server is an integral part of VMware’s infrastructure, designed to facilitate management and monitoring of physical and virtual components within a virtualized environment. CIM is a standard used for representing system components in a unified manner, ensuring interoperability between hardware, hypervisors, and management tools. In VMware environments, the CIM server enables communication between vCenter, ESXi hosts, and the underlying hardware to monitor system health, performance, and events in real-time.
Server and Infrastructure Solutions
VMware provides an extensive range of server and infrastructure solutions that are designed to meet the needs of businesses, from small-scale operations to large enterprise environments. These solutions offer robust virtualization capabilities, streamline resource management, and enable businesses to transition to hybrid and multi-cloud environments effectively. In this section, we’ll cover some of VMware’s essential technologies, including VMware Server, ESXi, Horizon, and the difference between ESX and ESXi.
What Is VMware Server?
VMware Server is a free virtualization product that allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single physical machine, enabling efficient use of resources. Released in the early 2000s, VMware Server targeted businesses and IT professionals who needed basic virtualization capabilities without requiring complex infrastructure. It provided an easy-to-use platform for running and testing multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a host operating system, such as Windows or Linux.
What Is ESXi VMware? An In-Depth Guide
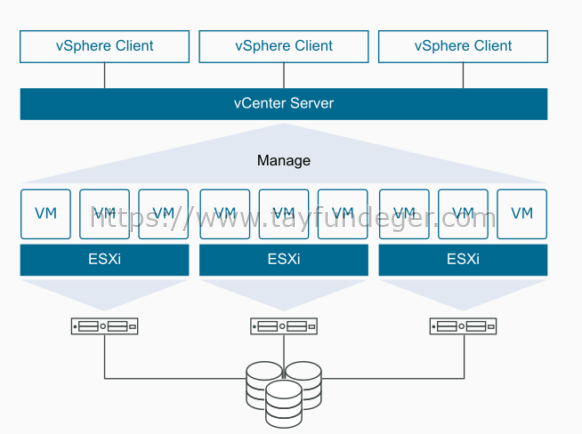
VMware ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor, meaning it runs directly on hardware without the need for a traditional operating system. As one of VMware’s core virtualization solutions, ESXi allows administrators to create, manage, and run multiple VMs on a single physical server. It’s widely regarded for its lightweight footprint, high efficiency, and ability to consolidate workloads while minimizing hardware expenses.
What Is Horizon VMware? Virtual Desktop Infrastructure Explained
VMware Horizon is a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solution that delivers desktops and applications to end-users through virtualization. It enables businesses to centralize desktop environments in a data center or cloud while allowing users to access them remotely from various devices, such as laptops, tablets, or thin clients. With VMware Horizon, organizations can provide a consistent user experience across devices while improving security and reducing management overhead.
What Is VMware ESX? Difference Between ESX and ESXi
VMware ESX was the original hypervisor released by VMware as part of its virtualization offerings. It served as the foundation for VMware’s early virtualization products but has since been replaced by ESXi. Understanding the differences between ESX and ESXi helps clarify the evolution of VMware’s hypervisor technology.
VMware in Business and Industry

VMware has transformed the way businesses operate by offering cutting-edge virtualization, cloud, and digital workspace solutions. Across industries, organizations rely on VMware to optimize IT operations, enhance security, and enable remote work. From healthcare and finance to retail and education, VMware’s suite of products helps businesses reduce infrastructure costs, improve operational efficiency, and accelerate digital transformation. By adopting VMware’s solutions, enterprises can create scalable IT environments, ensuring seamless operations whether on-premises or in the cloud.
What Is Broadcom Doing with VMware? Business Insights
In 2021, Broadcom announced its plan to acquire VMware, setting the stage for a significant shift in both companies’ strategic direction. This acquisition reflects Broadcom’s intention to expand beyond its traditional hardware focus into software and cloud infrastructure, aligning itself with the growing demand for digital transformation solutions. VMware’s extensive virtualization technologies—such as vSphere, NSX, and Tanzu—present Broadcom with a unique opportunity to build a comprehensive portfolio that blends hardware, software, and cloud technologies.
What Is AirWatch by VMware?
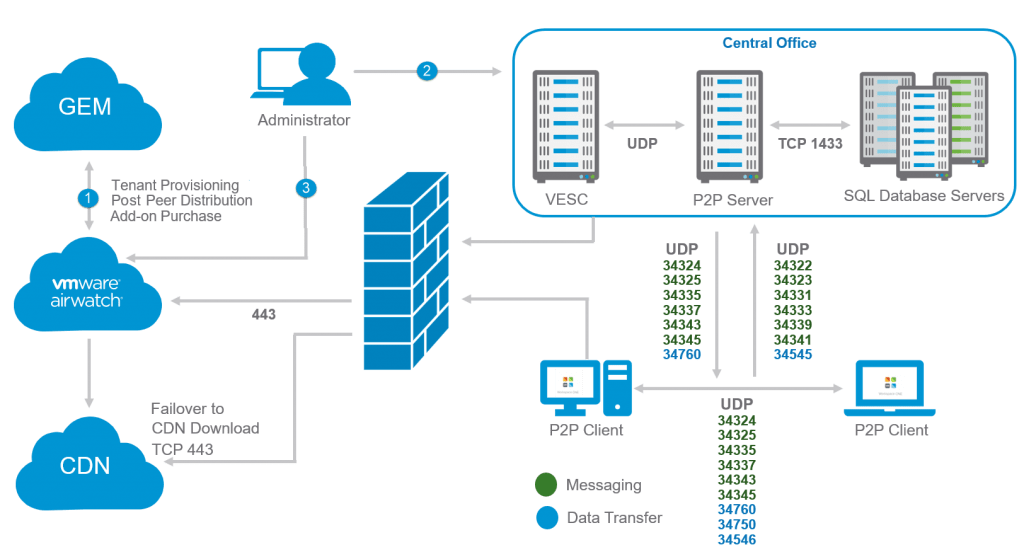
AirWatch by VMware is a comprehensive enterprise mobility management (EMM) solution designed to help organizations manage and secure mobile devices, apps, and data across multiple platforms. Initially founded as a standalone company, AirWatch was acquired by VMware in 2014, enhancing VMware’s digital workspace offerings. This solution allows companies to control employee devices, enforce security policies, and enable access to enterprise applications from any location.
What Is AirWatch VMware? Mobile Device Management Solution
AirWatch by VMware is a critical component of VMware Workspace ONE, a unified endpoint management (UEM) platform. AirWatch enables companies to monitor, manage, and secure mobile devices used by employees, making it easier for organizations to implement remote work policies. The mobile device management (MDM) capabilities provided by AirWatch allow IT administrators to oversee a wide array of endpoints—including smartphones, tablets, and laptops—from a centralized dashboard. This unified view simplifies device configuration, software updates, and policy enforcement across all endpoints, ensuring compliance with corporate security standards.
Practical Use Cases and Deployment
VMware offers a suite of virtualization technologies that have transformed how businesses and individuals manage computing resources. From data centers to personal devices, VMware provides tools for everything from virtual desktops to cloud infrastructure. This section dives deep into VMware’s practical applications, its role across industries, and the components necessary for smooth deployments.
What Is VMware Used For? Real-World Applications
VMware’s virtualization technology is widely used across various environments to optimize infrastructure, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency. A primary use case is server virtualization, where physical servers are divided into multiple virtual machines (VMs), each running its operating system and applications. This reduces the need for additional physical servers, saving space, energy, and maintenance costs.
What Industries Use VMware? Key Sectors Benefiting from Virtualization
VMware has become essential across multiple industries due to its versatility and ability to streamline IT operations. In finance and banking, VMware ensures uninterrupted service by offering high availability and disaster recovery solutions, safeguarding sensitive data. Healthcare providers rely on VMware to host critical applications, such as electronic health records (EHR) systems, and enable secure remote access for healthcare professionals.
What Is a VMware Image? How Virtual Machines Are Packaged
A VMware image is a complete, encapsulated copy of a virtual machine, including its operating system, software applications, and configuration settings. These images allow easy deployment of VMs across different environments and are often used to create backups or distribute pre-configured environments. VMware images are typically saved in formats such as OVA (Open Virtual Appliance) or OVF (Open Virtualization Format), making them portable across various hypervisors.
What Is a VMware Host? Managing Virtual Environments
In VMware’s virtualization framework, a VMware host refers to the physical server or machine that runs multiple virtual machines (VMs) using a hypervisor, such as VMware ESXi. The host serves as the foundational infrastructure, providing the hardware resources—CPU, memory, storage, and networking—necessary for VMs to operate. In a virtualized data center, multiple VMware hosts are often pooled together to form clusters managed by vCenter Server for centralized management.
What Is a VMware Port Group?
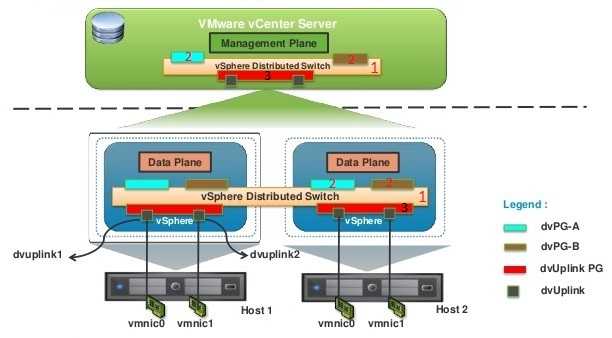
A VMware port group is a logical entity that helps organize and manage network traffic within a virtualized environment. Port groups are part of virtual switches (vSwitches), which act as software-defined networking devices on a VMware host. Each virtual machine connected to a port group receives the same networking configuration, such as VLAN settings, security policies, and traffic-shaping rules.
Comparisons and Alternatives
When deciding on the right virtualization or cloud solution, users often compare VMware with other platforms like VirtualBox, Hyper-V, and AWS. Each platform offers unique features and strengths, making them suitable for different use cases. In this section, we’ll explore how VMware stacks up against other popular alternatives to help you make an informed decision.
What Is Better, VMware or VirtualBox?
VMware and VirtualBox are two of the most popular virtualization platforms, but they serve slightly different audiences. VMware is generally known for professional use, offering high performance and advanced features for businesses and enterprises. On the other hand, VirtualBox is an open-source virtualization platform primarily used for personal and academic purposes.
VMware Workstation (for Windows and Linux) and VMware Fusion (for macOS) provide more powerful functionality, including support for complex networking configurations and higher efficiency in managing virtual machines. VMware also offers more robust support for 3D acceleration, making it ideal for resource-heavy applications.
VMware vs Hyper-V: Which Platform Is Better?
VMware and Hyper-V are leading virtualization platforms, but they cater to different needs and infrastructure requirements. Hyper-V, developed by Microsoft, is tightly integrated with Windows Server and Azure, making it an excellent choice for companies that already use Microsoft’s ecosystem. On the other hand, VMware’s hypervisors (like ESXi) are more feature-rich and widely adopted across industries, providing better flexibility for organizations using hybrid environments.
Performance and Resource Management: VMware excels in live migration with vMotion, offering seamless migration of VMs without downtime. Hyper-V also provides live migration but with more limitations, especially in cross-platform environments. VMware’s DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) optimizes resource allocation more efficiently compared to Hyper-V’s resource management tools.
Licensing and Cost: Hyper-V offers a more affordable solution, especially since it comes bundled with Windows Server licenses. However, VMware offers more mature and sophisticated virtualization capabilities for companies willing to invest in premium tools.
Ultimately, VMware is often favored by organizations with complex virtualization needs, while Hyper-V is ideal for Windows-centric environments looking for cost-effective solutions.
VMware vs AWS: A Cloud Platform Comparison
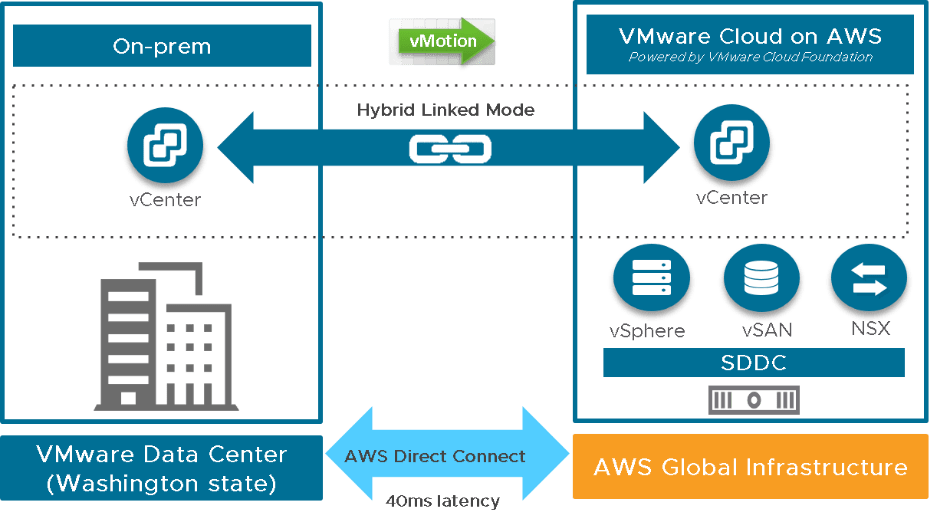
VMware and AWS (Amazon Web Services) serve different purposes: VMware focuses on virtualization and private cloud infrastructure, while AWS is a public cloud platform offering a wide range of on-demand services such as compute power, storage, and machine learning tools. However, with the AWS VMware Cloud solution, these two platforms have found ways to complement each other.
Use Cases: VMware is ideal for organizations that require on-premises or hybrid cloud environments, especially when dealing with sensitive data or workloads that need to remain under local control. AWS, on the other hand, excels in scalability and cost-efficiency, making it a perfect solution for companies looking to quickly deploy cloud-based applications.
Integration: VMware Cloud on AWS enables businesses to extend their existing VMware infrastructure to the public cloud, providing seamless integration between private and public environments. This makes it easier for organizations to move workloads between VMware’s on-premises infrastructure and AWS’s cloud resources.
What Is VMware Workstation vs Fusion? Key Differences
VMware Workstation and VMware Fusion are two desktop virtualization tools offered by VMware, but they cater to different operating systems and use cases. VMware Workstation is designed for Windows and Linux users, while VMware Fusion is optimized for macOS users.
Use Cases: VMware Workstation is popular among IT professionals and developers who need to test software across multiple operating systems. It supports complex networking, scripting, and integration with VMware’s enterprise platforms, such as vSphere. In contrast, VMware Fusion is better suited for macOS users who need to run Windows or Linux applications on their Mac without rebooting. Fusion offers smooth integration with macOS features, including drag-and-drop functionality between the host and guest operating systems.
Performance: Both Workstation and Fusion offer high performance for running multiple VMs simultaneously. However, Workstation Pro supports more advanced features such as shared virtual networks and cloning, which make it ideal for enterprise development and testing environments. Fusion offers Unity mode, a unique feature that allows Windows apps to run seamlessly within macOS.
If you are a Windows or Linux user, VMware Workstation provides a more powerful set of tools for professional use. For macOS users, VMware Fusion offers an excellent way to run Windows applications without compromising the macOS experience.
Setup, Configuration, and Troubleshooting
VMware provides a range of virtualization solutions that streamline IT infrastructure, increase flexibility, and improve resource management. However, setting up, configuring, and troubleshooting VMware tools effectively requires understanding various processes. This guide breaks down essential steps and procedures for managing VMware products such as VMware Workstation, VMware Horizon Client, VMware Tools, and vCenter. Each section offers step-by-step insights to help users set up virtual environments smoothly and troubleshoot issues when needed.
How to Set Up VMware Workstation on Windows
VMware Workstation is a popular virtualization platform that allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single machine. To install it on Windows, first, download the VMware Workstation installer from VMware’s official site. After the download, run the installer as an administrator. Follow the prompts, accept the license agreement, and select the desired installation folder. You may enable or disable additional options, like creating desktop shortcuts.
How to Configure VMware Horizon Client
VMware Horizon Client is used to connect to virtual desktops and remote applications, enabling seamless access across devices. To configure the Horizon Client, download it from VMware’s website, and install it on your device. After installation, open the Horizon Client, and click “Add Server.” Enter the connection server’s IP address or URL, usually provided by your IT administrator.
How to Install VMware Tools on a Virtual Machine
VMware Tools is a vital component that enhances the performance and functionality of virtual machines. It improves video performance, mouse synchronization, and copy-paste operations between the host and guest operating systems. To install VMware Tools, first, power on the virtual machine in VMware Workstation or vSphere. Navigate to VM > Install VMware Tools from the top menu.
How to Create a Virtual Machine Using VMware Workstation
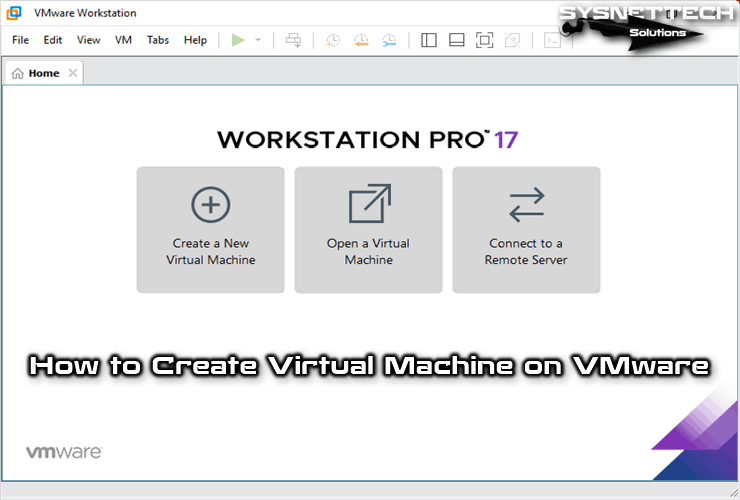
Creating a virtual machine (VM) in VMware Workstation is straightforward, allowing you to test different operating systems or run software in isolated environments. Begin by opening VMware Workstation and selecting “Create a New Virtual Machine.” You’ll be given two options: Typical (recommended for quick setups) or Custom (for advanced configurations). Choose your preferred method and select the installation media, such as an ISO file or physical disk.
How to Use VMware vCenter for Environment Management
VMware vCenter is a centralized platform used to manage multiple ESXi hosts and virtual machines efficiently. It allows administrators to automate tasks, monitor performance, and streamline resource allocation. To use vCenter, first ensure that the vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) is deployed and accessible via a web browser. Log into the vCenter interface using your credentials.
How to Perform Live Migration with VMware vMotion
VMware vMotion allows administrators to migrate running virtual machines between ESXi hosts without downtime. This feature ensures high availability and load balancing, especially in production environments. To perform a vMotion migration, ensure that both the source and destination hosts are connected to shared storage and are part of the same vCenter cluster.
How to Troubleshoot VMware Network Issues
Network issues in VMware environments can be caused by misconfigurations, faulty virtual adapters, or incorrect IP settings. The first step in troubleshooting is to identify whether the issue lies in the virtual network (such as port groups or virtual switches) or the physical network infrastructure. Use vCenter or the ESXi host interface to verify the status of virtual switches, port groups, and adapters.
Advanced VMware Topics
What Is an OVA VMware Appliance?
An OVA (Open Virtual Appliance) is a file format that encapsulates a complete virtual machine (VM) into a single, portable package. This format is designed for easy distribution and deployment of VMs across different virtualization platforms, particularly VMware environments. An OVA file typically contains an OVF (Open Virtualization Format) descriptor file, which provides metadata about the VM, along with its virtual disk files. This means that when you download an OVA file, you’re getting everything you need to set up a virtual machine, including the operating system, application software, and configuration settings.
What Is a VMware Datastore Used For?
A VMware datastore is a storage location used to hold virtual machine files, including virtual disks (VMDKs), snapshots, and configuration files. Datastores can be based on various storage types, such as Network File System (NFS), Fibre Channel, or iSCSI, making them flexible and adaptable to different infrastructure requirements. The choice of datastore type often depends on the performance needs, scalability, and budget considerations of an organization.
What Is Bridged Network in VMware?
A bridged network in VMware refers to a networking configuration that connects a virtual machine directly to the physical network. In this setup, the VM appears as a separate entity on the network, allowing it to obtain an IP address from the same DHCP server as the physical host. This means that the virtual machine can communicate with other machines on the network as if it were a physical computer, enabling seamless integration into existing network resources.
What Is a Clone in VMware? Differences from Snapshots

In VMware, a clone is an exact copy of a virtual machine that includes its entire state, including the operating system, applications, and data. Clones can be created for various purposes, such as testing new applications, troubleshooting issues, or deploying multiple instances of a VM with the same configuration. Cloning is particularly useful when an organization wants to maintain consistency across multiple virtual machines without manually configuring each one.
What Is Bootbank in VMware? Overview of Configuration Partitions
The bootbank in VMware refers to a specific partition on a VMware ESXi host that contains essential boot files and configuration settings. This partition is critical for the ESXi host to function correctly, as it holds the files necessary for the boot process and the basic configuration of the host. Understanding the role of the bootbank is vital for administrators tasked with managing and maintaining VMware environments.
Licensing, Pricing, and Certification
Understanding VMware’s licensing, pricing, and certification is crucial for businesses and IT professionals looking to leverage VMware’s powerful virtualization technology. VMware provides various products that require different licensing models, pricing plans, and certifications, making it essential to navigate these aspects effectively to maximize the benefits of their software. This guide will explore VMware’s pricing plans, certification programs, and licensing models, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of these key components.
What Are VMware’s Pricing Plans?
VMware offers a variety of pricing plans tailored to meet the needs of different customers, whether they are small businesses, large enterprises, or educational institutions. Generally, VMware’s pricing structure is subscription-based, allowing users to pay annually for access to its software and services. For instance, the VMware vSphere product line, which is pivotal for virtualization and cloud infrastructure, typically comes with multiple tiers. The Standard, Enterprise, and Enterprise Plus editions each provide different features, capabilities, and resource limits, catering to the specific needs of various organizations.
How to Get VMware Certified: Certification Programs Overview
Achieving VMware certification is an invaluable asset for IT professionals seeking to enhance their skills and career prospects in virtualization and cloud technologies. VMware offers a range of certification programs designed to validate expertise in various VMware products and solutions, ensuring that certified professionals possess the knowledge required to implement and manage VMware environments effectively.
VMware Licensing Models Explained
VMware’s licensing models are designed to offer flexibility and scalability, allowing organizations to choose the best option that aligns with their operational requirements. The most common licensing models include perpetual licenses, subscription licenses, and term licenses. Each of these models comes with unique benefits and considerations that organizations must evaluate before making a decision.
Perpetual licenses provide users with indefinite access to a specific version of VMware software, requiring a one-time purchase fee. This model is advantageous for organizations that prefer to invest upfront and do not want to deal with ongoing subscription costs. However, perpetual licenses typically come with limited support and updates unless organizations choose to purchase maintenance agreements separately, which can add to the total cost over time.
Future of VMware
As virtualization technology continues to evolve, VMware remains at the forefront of innovation, paving the way for future advancements in cloud computing and digital transformation. The company has consistently adapted its offerings to meet the dynamic needs of businesses, focusing on solutions that enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall IT performance. With the increasing demand for hybrid and multi-cloud environments, VMware is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of IT infrastructure.
What Is VMware Doing in the Cloud?
VMware is actively expanding its cloud offerings to meet the growing demand for flexible and scalable solutions. With the advent of cloud computing, organizations are increasingly looking for ways to leverage the cloud for their IT needs, and VMware is well-positioned to provide robust solutions that cater to these demands. The company’s strategy focuses on enabling seamless integration between on-premises infrastructure and public and private clouds, creating a unified environment for managing workloads.
How VMware Is Innovating with Tanzu for Kubernetes
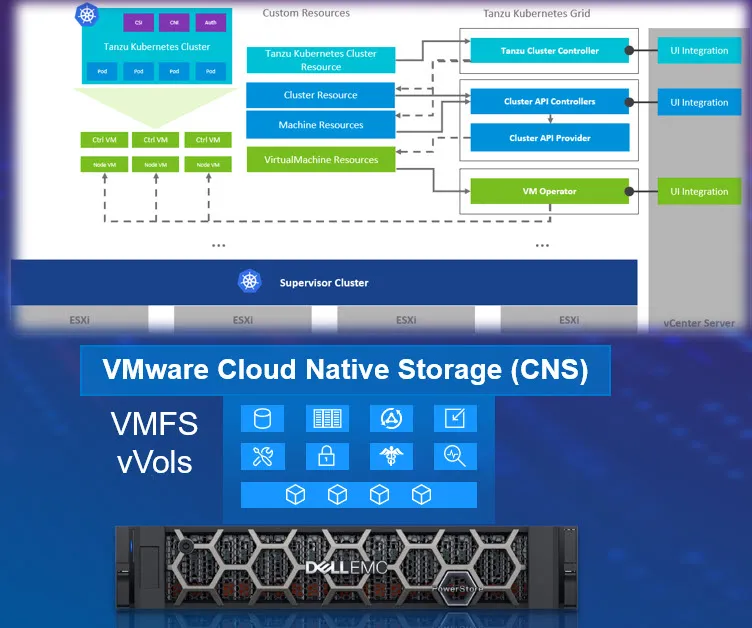
VMware’s investment in Kubernetes through its Tanzu platform represents a significant leap forward in cloud-native application development and management. Tanzu simplifies the deployment and management of containerized applications, enabling developers to build and run applications across various environments with ease. This innovation reflects VMware’s commitment to helping organizations navigate the complexities of modern application architectures.
What Is Broadcom’s Acquisition of VMware? Impact on the Market
Broadcom’s acquisition of VMware marks a pivotal moment in the tech industry, signaling significant changes in the landscape of virtualization and cloud computing. Announced in May 2022, the acquisition aimed to combine Broadcom’s semiconductor expertise with VMware’s virtualization and cloud technologies, creating a powerhouse capable of delivering integrated solutions for enterprise customers.
Miscellaneous VMware Topics
As the landscape of IT continues to evolve, VMware remains at the forefront of virtualization technology. Understanding various VMware concepts and tools can significantly enhance your ability to optimize resources, manage infrastructure, and support remote work environments. In this article, we’ll explore key VMware topics, including Software-Defined Data Centers (SDDC), the distinctions between VMware appliances and virtual machines, how to utilize VMware Player for free virtualization, and the benefits of VMware Workspace ONE for remote work.
What Is VMware SDDC? Software-Defined Data Center Explained
A Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) represents a transformative approach to managing data center resources through virtualization technologies. In an SDDC, all components of the data center, including compute, storage, and networking, are virtualized and delivered as a service. VMware SDDC integrates various VMware solutions, such as vSphere, vSAN, and NSX, to create a cohesive infrastructure that can be managed centrally. This model allows for greater flexibility and scalability, enabling organizations to respond rapidly to changing business needs.
What Is VMware Appliance vs Virtual Machine?
When discussing VMware environments, the terms “appliance” and “virtual machine” often arise, leading to confusion about their meanings. A VMware appliance is a pre-configured virtual machine image designed for specific tasks or services. These appliances bundle the operating system, applications, and necessary settings into a single, ready-to-deploy package. This makes them incredibly user-friendly, allowing administrators to quickly implement complex services without extensive setup or configuration.
How to Use VMware Player for Free Virtualization
VMware Player is a free, streamlined virtualization software that allows users to run virtual machines on their desktops or laptops. It provides an excellent entry point for individuals or small businesses looking to explore virtualization without the financial commitment associated with other VMware products. To get started with VMware Player, users need to download and install the application from the official VMware website. The installation process is straightforward, requiring just a few clicks to complete.
What Is VMware Workspace ONE for Remote Work?
VMware Workspace ONE is an integrated digital workspace platform designed to manage and secure remote work environments. In today’s business landscape, where remote work is becoming increasingly prevalent, Workspace ONE offers organizations the tools they need to ensure seamless access to applications and data from any device. By combining identity management, endpoint management, and application delivery into a single platform, Workspace ONE simplifies the IT experience while enhancing security protocols.