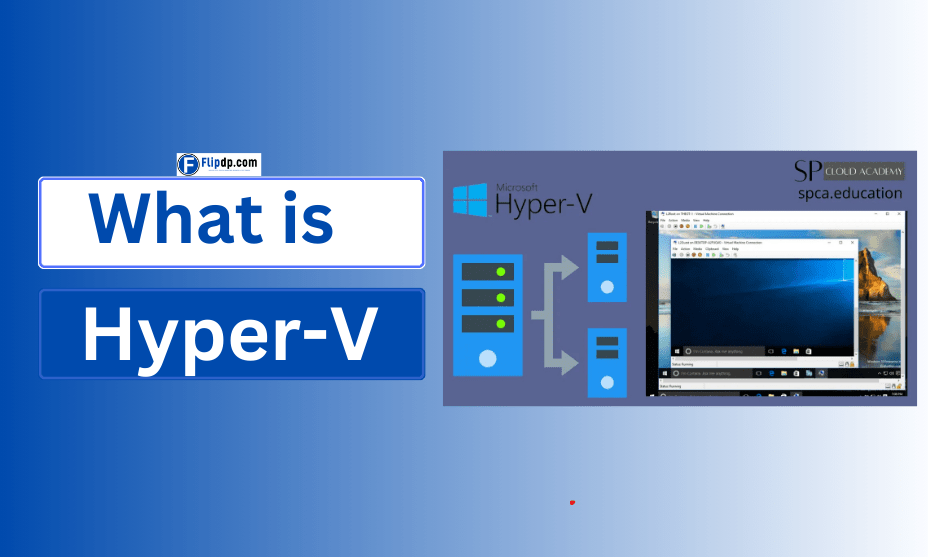
What is Hyper-V?
Hyper-V is a native hypervisor developed by Microsoft that enables the creation and management of virtual machines (VMs). It allows multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical server, essentially creating a virtualized environment. This virtualization technology is built into Windows Server and Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions.
Key Terminology:
- Virtual Machine (VM): A software-based emulation of a physical computer that runs an operating system and applications.
- Hypervisor: The software layer that enables virtualization by managing the interaction between the host system and the VMs.
Key Features of Hyper-V
Hyper-V comes with a robust set of features designed to enhance virtualization and improve overall IT management. Some key features include:
1. Virtual Networking
Hyper-V supports various networking options, allowing users to create virtual switches that manage traffic between VMs and the external network. This feature enables enhanced security and isolation.
2. Resource Allocation
Hyper-V allows for dynamic resource allocation. Administrators can allocate CPU, memory, and storage to VMs as needed, optimizing resource utilization and performance.
3. Live Migration
With Hyper-V, you can move VMs between physical hosts without downtime. This feature is particularly useful for maintenance tasks, load balancing, and disaster recovery.
4. Snapshots
Hyper-V allows users to create snapshots of VMs at a specific point in time. This feature is beneficial for backup and recovery, enabling administrators to revert to a previous state if necessary.
5. Hyper-V Replica
Hyper-V Replica provides disaster recovery solutions by creating copies of VMs in a secondary location. This feature ensures business continuity in the event of hardware failure or other disasters.
6. Integration Services
Hyper-V Integration Services enhance the performance of VMs by providing drivers and services that improve communication between the host and the VM.
How Does Hyper-V Work?
Hyper-V operates by creating a virtual environment on a physical server. Here’s a breakdown of its core functionalities:
1. Layered Architecture
Hyper-V utilizes a layered architecture, with the hypervisor sitting between the hardware and the operating system. This structure allows it to efficiently manage the resources allocated to each VM.
2. Virtual Machine Management
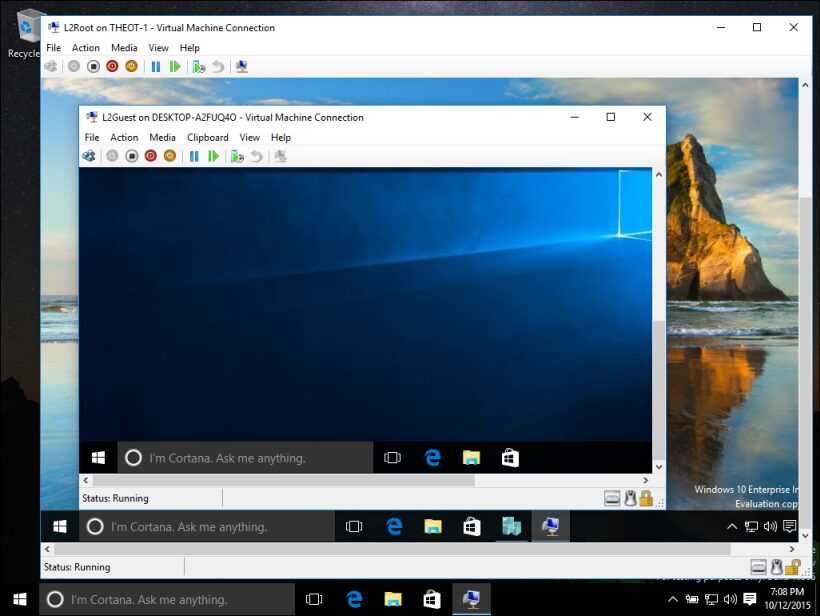
Hyper-V includes a management console known as Hyper-V Manager, which provides a graphical interface for creating, configuring, and managing VMs. It also integrates with System Center Virtual Machine Manager for more advanced management capabilities.
3. Resource Allocation and Management
The hypervisor allocates physical resources (CPU, RAM, and storage) to each VM based on predefined configurations. Users can adjust these allocations dynamically, ensuring optimal performance.
4. Security Features
Hyper-V employs various security measures, including secure boot, shielded VMs, and isolation techniques that protect the host and VMs from unauthorized access and threats.
Installation and Configuration

Installing Hyper-V is a straightforward process. Here’s how to do it:
Requirements:
- A compatible version of Windows (Windows Server or Windows 10 Pro/Enterprise).
- Hardware support for virtualization (Intel VT or AMD-V).
Installation Steps:
- Open Control Panel: Navigate to Programs > Turn Windows features on or off.
- Enable Hyper-V: Check the box for Hyper-V and click OK. The installation may take a few minutes.
- Restart the Computer: A system restart is required to complete the installation.
- Configure Hyper-V: Use Hyper-V Manager to create and manage virtual machines.
Creating a Virtual Machine:
- Open Hyper-V Manager.
- Click on “New” and select “Virtual Machine.”
- Follow the wizard to configure the VM’s settings, including memory, storage, and network connections.
- Install the operating system on the VM using a bootable image or installation media.
Use Cases for Hyper-V
Hyper-V is versatile and can be applied across various sectors and use cases. Some common applications include:
1. Server Consolidation
Businesses can reduce hardware costs by running multiple servers on a single physical machine, optimizing resource usage and minimizing energy consumption.
2. Development and Testing Environments
Hyper-V provides isolated environments for developers to test applications without affecting the production environment. This feature accelerates the software development lifecycle.
3. Disaster Recovery Solutions
With features like Hyper-V Replica, organizations can implement effective disaster recovery strategies, ensuring business continuity in case of hardware failures or disasters.
4. Desktop Virtualization
Hyper-V supports Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), allowing organizations to deliver virtual desktops to users. This setup improves manageability and enhances security.
Benefits of Using Hyper-V

Implementing Hyper-V can yield numerous benefits for organizations, including:
1. Cost Efficiency
By consolidating physical servers, businesses can significantly reduce hardware costs, energy consumption, and cooling requirements.
2. Improved Flexibility and Scalability
Hyper-V allows for easy scaling of resources based on demand. Organizations can quickly create or remove VMs as needed, adapting to changing business requirements.
3. Enhanced Security
With built-in security features and isolation techniques, Hyper-V helps protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access.
4. Simplified Management
Hyper-V Manager and integration with System Center streamline the management of virtual environments, reducing the administrative burden on IT staff.
Common Challenges and Misconceptions

While Hyper-V offers many advantages, some challenges and misconceptions can hinder its adoption:
1. Performance Overhead
One common misconception is that virtualization introduces significant performance overhead. While there is some overhead, Hyper-V is designed to minimize it, and many organizations report performance levels comparable to physical servers.
2. Complexity in Configuration
New users may find the initial setup and configuration of Hyper-V complex. However, numerous resources and guides are available to simplify this process.
3. Licensing Costs
Although Hyper-V is free with Windows Server, some users believe that the associated licensing costs for Windows Server can be prohibitive. It’s essential to evaluate the total cost of ownership versus potential savings.
4. Limited Support for Non-Windows Environments
While Hyper-V is primarily designed for Windows environments, it can support Linux VMs as well. However, managing mixed OS environments may require additional configuration and expertise.
Conclusion
Hyper-V is a powerful virtualization platform that plays a crucial role in modern IT infrastructures. By understanding what Hyper-V is, how it operates, and its numerous benefits, organizations can leverage this technology to optimize resource utilization, enhance security, and ensure business continuity.
FAQs, what is Hyper-V
1. What is Hyper-V?
Hyper-V is a virtualization platform developed by Microsoft that allows users to create and manage virtual machines (VMs). It enables multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server or computer, helping to maximize hardware utilization.
2. What are the benefits of using Hyper-V?
Hyper-V offers several benefits, including better resource utilization, isolation of workloads, flexibility for testing and development, and the ability to run different operating systems concurrently on the same hardware.
3. What are the system requirements for Hyper-V?
Hyper-V requires a 64-bit processor that supports hardware virtualization (Intel VT or AMD-V) and Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). It also requires a minimum of 4 GB of RAM, but more is recommended for running multiple VMs.
4. Which operating systems are compatible with Hyper-V?
Hyper-V can host a variety of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD. It is available on Windows Server and some versions of Windows 10 and 11.
5. How is Hyper-V different from other virtualization platforms like VMware?
Hyper-V is integrated with Windows and provides strong support for Windows workloads, while VMware is a widely-used cross-platform virtualization tool. Hyper-V is often preferred in Windows-centric environments, whereas VMware might be preferred for its broader feature set across platforms.