What Are Segmentation Targeting And Positioning: Complete Guide

what are segmentation targeting and positioning, In today’s competitive business landscape, understanding the intricacies of segmentation, targeting, and positioning (often abbreviated as STP) is vital for any marketing strategy. Companies that effectively apply these concepts can not only identify and reach their ideal customers but also create a distinct brand identity that resonates with their audience. This comprehensive guide will explore what segmentation, targeting, and positioning mean in marketing, their importance in business strategy, and how they work together to drive success. By the end of this article, you’ll have a deeper understanding of these concepts and practical insights to apply in your business.
Understanding Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning in Marketing

Segmentation, targeting, and positioning are foundational components of a successful marketing strategy. Together, they help businesses refine their marketing efforts and align their products or services with the right audience.
- Segmentation involves dividing a broad market into smaller segments based on shared characteristics.
- Targeting focuses on selecting specific segments to serve.
- Positioning is about creating a unique image of a product or brand in the minds of the target audience.
This STP model is a systematic approach that guides marketers in making strategic decisions about their offerings and promotional activities.
The Importance of Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning in Business Strategy
Implementing an effective STP strategy can significantly impact a company’s bottom line. Here are some critical reasons why these concepts are essential:
- Enhanced Customer Insights: By segmenting the market, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and needs, allowing for more tailored marketing efforts.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Targeting specific segments enables companies to allocate their marketing resources more effectively, ensuring that they reach those most likely to convert.
- Competitive Advantage: A well-defined positioning strategy helps companies differentiate themselves from competitors, creating a unique selling proposition (USP) that appeals to their target audience.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: When businesses understand their customers and effectively communicate their value proposition, they can foster stronger relationships, leading to increased customer loyalty and retention.
What is Market Segmentation? A Deep Dive

Market segmentation is the process of dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors. By segmenting the market, businesses can tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to meet the specific demands of each group.
The segmentation process typically involves identifying the criteria for segmenting the market and analyzing the resulting segments to determine their viability for targeting. Effective segmentation allows businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific audiences, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Types of Market Segmentation: Geographic, Demographic, Psychographic, and Behavioral
Market segmentation can be categorized into four primary types:
- Geographic Segmentation: Divides the market based on geographical areas such as countries, regions, cities, or neighborhoods. For example, a clothing brand may offer winter apparel in colder regions and lighter fabrics in warmer climates.
- Demographic Segmentation: Segments the market based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education level, and family size. For instance, a luxury car brand may target high-income individuals, while a toy company may focus on families with young children.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Focuses on the psychological aspects of consumers, including their lifestyles, values, interests, and personalities. A fitness brand, for example, may target health-conscious individuals who prioritize wellness.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Groups consumers based on their behaviors related to the product, such as purchase history, usage frequency, brand loyalty, and benefits sought. An example would be a software company that targets frequent users of its product with loyalty rewards.
How to Effectively Segment Your Market: Strategies and Techniques
To effectively segment your market, consider the following strategies:
- Conduct Market Research: Utilize surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gather data on consumer preferences and behaviors.
- Analyze Competitor Strategies: Study how competitors segment their markets and identify gaps that your business can exploit.
- Use Data Analytics Tools: Leverage data analytics software to analyze large datasets and identify patterns that can inform your segmentation strategy.
- Test Different Segments: Implement A/B testing to determine which segments respond best to your marketing efforts.
Benefits of Market Segmentation for Businesses
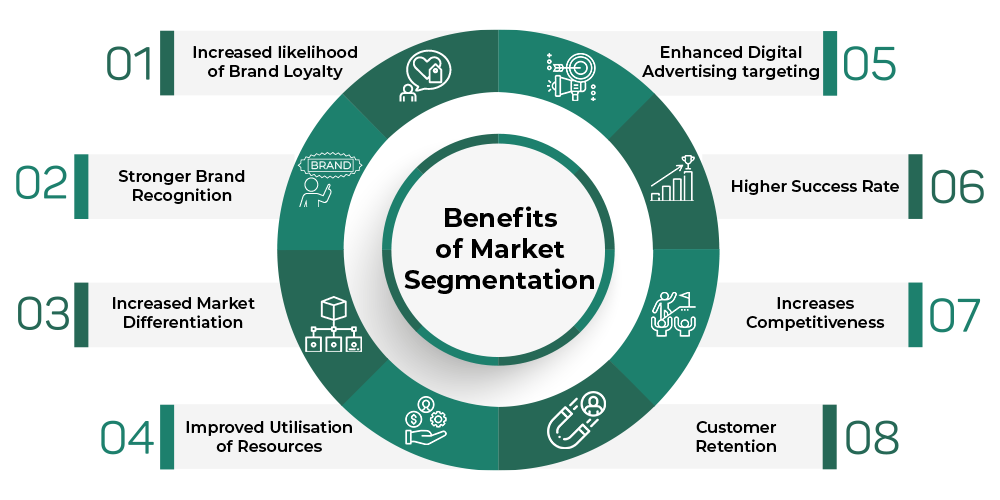
Market segmentation offers several advantages, including:
- Improved Marketing Efficiency: By targeting specific segments, businesses can create more relevant and compelling marketing messages that resonate with their audience.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: Tailored offerings often lead to higher conversion rates, resulting in increased sales and revenue.
- Better Customer Relationships: Understanding the unique needs and preferences of different segments allows businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers.
- Enhanced Product Development: Insights gained from segmentation can inform product development, leading to offerings that better meet consumer demands.
Common Mistakes in Market Segmentation and How to Avoid Them
Businesses often make mistakes in market segmentation that can hinder their success. Common pitfalls include:
- Over-Segmentation: Dividing the market into too many segments can complicate marketing efforts and dilute brand messaging. Focus on a manageable number of segments that align with your business objectives.
- Ignoring Market Changes: Consumer preferences and market conditions change over time. Regularly revisit and adjust your segmentation strategy to stay relevant.
- Lack of Research: Failing to conduct adequate market research can lead to misguided segmentation efforts. Invest in thorough research to ensure that your segments are based on data, not assumptions.
What is Targeting in Marketing? Defining Your Audience
Targeting refers to the process of selecting specific market segments to focus on and serve with tailored marketing efforts. It involves evaluating the potential of each segment and determining which ones align with your business goals and resources.
Effective targeting ensures that marketing messages reach the right audience, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
Different Targeting Strategies: Mass, Differentiated, Concentrated, and Micromarketing
Several targeting strategies can be employed, including:
- Mass Marketing: This approach targets the entire market with a single marketing strategy, often using a one-size-fits-all approach. An example would be a soft drink brand that aims to appeal to all consumers regardless of demographic or behavioral differences.
- Differentiated Marketing: In this strategy, businesses target multiple segments with distinct marketing messages tailored to each group. A cosmetics brand might offer different product lines for teenagers, adults, and seniors, each with its own marketing campaign.
- Concentrated Marketing: This strategy focuses on a single market segment, allowing businesses to specialize and serve that niche effectively. A vegan skincare company might choose to concentrate on environmentally conscious consumers.
- Micromarketing: Also known as localized marketing, this strategy targets individual customers or very small segments. For example, a local restaurant may create personalized offers for customers based on their previous dining history.
How to Choose the Right Target Market for Your Business
Selecting the right target market requires careful consideration of various factors:
- Market Size and Growth Potential: Evaluate the size and growth potential of each segment to determine its viability for targeting.
- Competition: Analyze the competitive landscape to identify segments with less competition, allowing for easier market entry.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Ensure that the selected target market aligns with your overall business objectives and capabilities.
- Consumer Needs and Preferences: Understand the specific needs and preferences of potential customers to tailor your offerings effectively.
The Role of Customer Personas in Targeting
Customer personas are fictional representations of your ideal customers based on market research and data analysis. They help businesses visualize their target audience and tailor marketing strategies accordingly.
Creating customer personas involves gathering information such as demographics, interests, pain points, and buying behaviors. By developing detailed personas, businesses can create more relevant content, design targeted marketing campaigns, and enhance overall customer engagement.
What is Positioning? Crafting Your Brand Identity
Positioning refers to the process of establishing a brand’s identity and unique value in the minds of consumers relative to competitors. It involves creating a perception of the brand that resonates with the target audience and differentiates it from other offerings in the market.
Effective positioning helps consumers understand what makes a brand unique and why they should choose it over alternatives. It is closely tied to the company’s overall branding strategy and is communicated through various marketing channels.
The Positioning Process: Steps to Effective Brand Positioning
The positioning process typically involves the following steps:
- Identify Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Determine what sets your product or service apart from competitors. This could be quality, price, features, or customer service.
- Understand Your Target Audience: Conduct research to understand the preferences, needs, and pain points of your target audience.
- Analyze Competitors: Assess how competitors position themselves in the market. Identify gaps or opportunities for differentiation.
- Develop a Positioning Statement: Create a clear and concise positioning statement that articulates your brand’s unique value and target audience. This statement should guide all marketing efforts.
- Communicate Your Positioning: Implement your positioning strategy across all marketing channels, including advertising, social media, and content marketing.
Differentiation Strategies: How to Stand Out in the Market
To successfully position your brand, consider employing differentiation strategies such as:
- Product Differentiation: Highlight unique features, quality, or benefits of your product that set it apart from competitors.
- Service Differentiation: Offer exceptional customer service or additional services that enhance the customer experience.
- Channel Differentiation: Use unique distribution channels to reach customers, ensuring that your product is accessible in ways that competitors may not be.
- Image Differentiation: Create a strong brand image through marketing, packaging, and branding efforts that resonate with your target audience.
- Pricing Differentiation: Position your brand as a premium or budget-friendly option, depending on your target market’s preferences and willingness to pay.
The Importance of a Unique Selling Proposition (USP) in Positioning
A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is a crucial element of effective positioning. It defines what makes your product or service unique and why customers should choose it over alternatives. A strong USP is clear, concise, and compelling, effectively communicating the brand’s value.
To create a powerful USP, consider the following:
- Understand Your Customers: Identify what matters most to your target audience, such as quality, price, convenience, or customer service.
- Analyze Competitors: Research competitors’ USPs to identify opportunities for differentiation. What do they offer, and how can you improve upon it?
- Focus on Benefits, Not Features: Emphasize the benefits that your product delivers to the customer rather than just listing features. How does it solve a problem or enhance their lives?
- Be Authentic: Ensure that your USP aligns with your brand’s values and identity. Authenticity fosters trust and loyalty among customers.
Integration of Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
How Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Work Together
Segmentation, targeting, and positioning are interconnected processes that, when executed effectively, lead to a cohesive marketing strategy. Here’s how they work together:
- Segmentation allows businesses to identify distinct groups within the broader market, focusing on shared characteristics and behaviors.
- Targeting involves selecting specific segments to pursue, aligning marketing efforts with the needs and preferences of those groups.
- Positioning creates a brand identity that resonates with the targeted audience, effectively communicating the unique value of the offering.
By integrating these three components, businesses can create a focused marketing strategy that enhances customer engagement, improves brand perception, and ultimately drives sales.
Case Studies: Successful Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning in Action
To illustrate the effectiveness of the STP model, let’s examine a few case studies of companies that have successfully implemented segmentation, targeting, and positioning strategies:
- Nike: Nike segments its market based on demographics, psychographics, and behavioral factors. They target different segments through tailored product lines (e.g., running shoes, lifestyle sneakers) and targeted marketing campaigns that speak to specific audiences, such as athletes and fashion-conscious consumers. Nike’s positioning as a premium athletic brand is reinforced by its “Just Do It” slogan and endorsements from high-profile athletes.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola employs geographic segmentation to tailor its marketing strategies to different regions. In the United States, they market traditional Coca-Cola, while in other countries, they may introduce unique flavors or lower-sugar options to cater to local tastes. Coca-Cola’s strong brand positioning as a refreshing and iconic beverage is consistent across its global campaigns, reinforcing its market leadership.
- Airbnb: Airbnb uses psychographic segmentation to target travelers seeking unique and local experiences. what are segmentation targeting and positioning By positioning itself as a platform for authentic travel, Airbnb differentiates itself from traditional hotels. The brand’s messaging emphasizes community, personal connections, and the opportunity to live like a local, which resonates with its target audience of adventurous and socially-conscious travelers.
Tools and Techniques for Implementing Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
To effectively implement segmentation, targeting, and positioning, businesses can utilize a variety of tools and techniques:
- Market Research Tools: Surveys, focus groups, and interviews can provide valuable insights into customer preferences and behaviors.
- Data Analytics Software: Tools like Google Analytics, Tableau, or HubSpot can help analyze customer data and identify segmentation opportunities.
- CRM Systems: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software can track customer interactions, enabling businesses to develop detailed customer personas for targeting.
- Social Media Analytics: Platforms like Facebook Insights and Twitter Analytics provide valuable data on audience demographics, behaviors, and preferences, aiding in segmentation efforts.
- A/B Testing Tools: Tools like Optimizely or Google Optimize can be used to test different marketing strategies and determine which resonates best with target segments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding segmentation, targeting, and positioning is essential for any business looking to thrive in today’s competitive market. By effectively segmenting the market, targeting specific audiences, and crafting a unique brand position, companies can create impactful marketing strategies that resonate with consumers and drive growth.
By implementing the insights and strategies outlined in this guide, businesses can enhance their marketing efforts, improve customer engagement, and ultimately achieve greater success. Remember that the STP model is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that should be regularly evaluated and adjusted to keep pace with changing consumer preferences and market dynamics.
FAQs, what are segmentation targeting and positioning
1. What is Segmentation in Marketing?
Segmentation in marketing refers to the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into smaller, more manageable groups of potential customers. These groups share common characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, or needs, allowing businesses to tailor their marketing efforts effectively.
2. What is Targeting in the STP Model?
Targeting is the process of selecting specific segments from a market that a business wants to focus its marketing efforts on. Once the market is segmented, the company decides which segments present the best opportunities based on factors like market size, profitability, and accessibility.
3. What is Positioning in Marketing?
Positioning refers to how a company wants its product or service to be perceived in the minds of the target audience. It involves creating a distinct image or identity for the product relative to competitors, emphasizing the benefits or unique selling propositions (USPs) that appeal to the selected target market.
4. Why is Segmentation Important in Marketing?
Segmentation helps businesses focus their efforts on specific groups of consumers. This approach enables personalized marketing strategies, improves customer satisfaction, and increases the efficiency of marketing campaigns by addressing the unique needs of each segment.
5. What Are the Common Types of Market Segmentation?
The most common types of market segmentation include:Demographic Segmentation: Based on age, gender, income, education, etc.
Geographic Segmentation: Based on location such as country, region, or city.
Psychographic Segmentation: Based on lifestyle, personality, or social status.
Behavioral Segmentation: Based on consumer behaviors like purchase habits or brand loyalty.





2 Comments