In the rapidly evolving landscape of wireless communication, GHz wireless technology has emerged as a pivotal force driving innovation and connectivity. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, understanding the nuances of GHz wireless technology becomes essential for both consumers and industry professionals. This comprehensive exploration delves into the benefits, applications, and future trends of GHz wireless technology, providing valuable insights into its transformative impact on modern society.
Introduction: The Quantum Leap in Wireless Communication
Imagine a world where your devices communicate seamlessly at lightning speeds, where connectivity is ubiquitous, and where the boundaries of technology are continually expanding. This is the promise of GHz wireless technology—a cornerstone of the digital age that is revolutionizing how we live, work, and interact. From powering the latest smartphones to enabling sophisticated IoT networks, GHz wireless technology is the invisible force propelling us into a connected future. But what exactly is GHz wireless technology, and why is it garnering so much attention? Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the intricacies of this groundbreaking technology.
Understanding GHz Wireless Technology
What is GHz Wireless Technology?
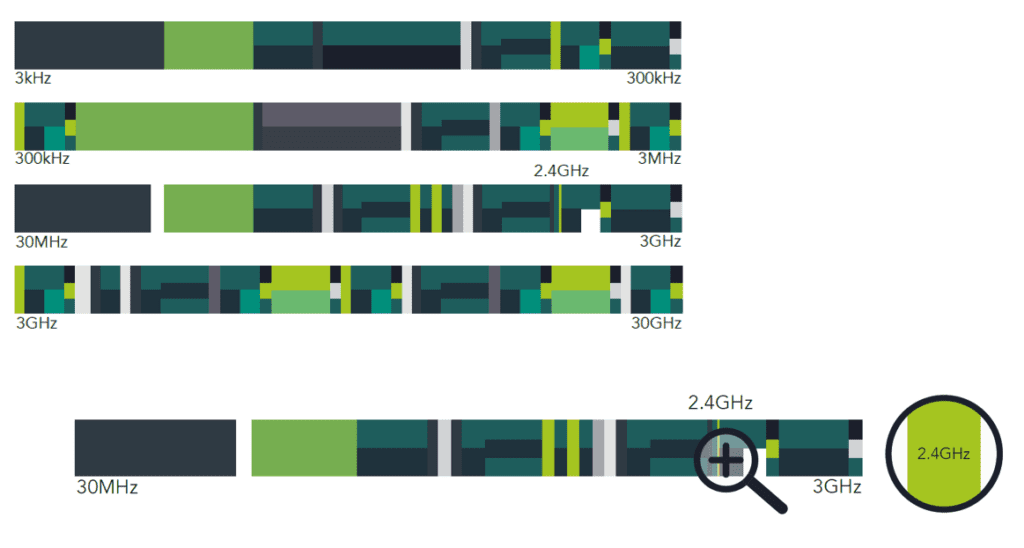
GHz wireless technology refers to wireless communication systems that operate in the gigahertz (GHz) frequency bands. A gigahertz is one billion cycles per second, and wireless technologies utilizing these frequencies are pivotal in delivering high-speed data transmission and robust connectivity. Common GHz bands used in wireless technology include 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and the emerging 60 GHz bands, each serving distinct purposes and offering unique advantages.
Key Frequency Bands Explained
- 2.4 GHz Band:
- Usage: Predominantly used for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other consumer electronics.
- Advantages: Excellent range and penetration through obstacles like walls.
- Limitations: Susceptible to interference from household devices (e.g., microwaves, cordless phones).
- 5 GHz Band:
- Usage: Enhanced Wi-Fi networks (Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6), some cordless phones.
- Advantages: Higher data rates, less interference, and more non-overlapping channels.
- Limitations: Shorter range and reduced ability to penetrate solid objects compared to 2.4 GHz.
- 60 GHz Band:
- Usage: Emerging applications like ultra-fast Wi-Fi (WiGig), wireless VR, and high-definition video streaming.
- Advantages: Extremely high data rates and low latency.
- Limitations: Very limited range and high sensitivity to physical obstructions.
How GHz Wireless Technology Works
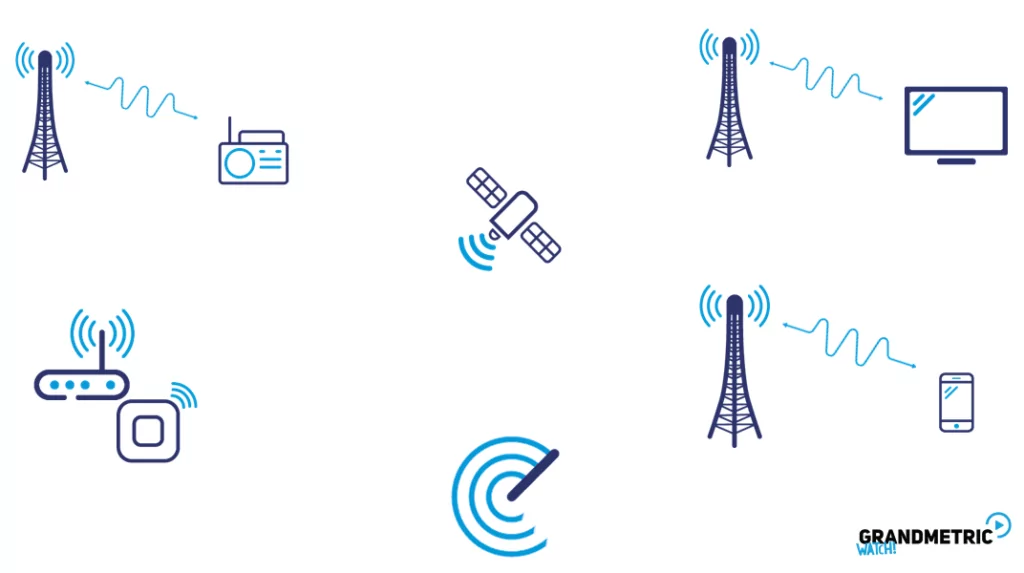
At its core, GHz wireless technology relies on radio waves to transmit data between devices. The frequency band determines the speed, range, and reliability of the connection. Higher frequencies, such as 60 GHz, can carry more data but have shorter ranges and are more easily blocked by obstacles. Conversely, lower frequencies like 2.4 GHz offer broader coverage but at slower speeds and with higher susceptibility to interference.
Advanced modulation techniques and multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technologies enhance the efficiency and capacity of GHz wireless networks, enabling faster and more reliable connections even in densely populated areas.
Benefits of GHz Wireless Technology
High-Speed Data Transmission
One of the most significant advantages of GHz wireless technology is its ability to facilitate high-speed data transmission. Higher frequency bands, particularly 5 GHz and 60 GHz, support faster data rates, making them ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and large file transfers. This ensures that users experience minimal lag and buffering, enhancing overall digital experiences.
Enhanced Connectivity and Reliability
GHz wireless technology offers robust and reliable connections, crucial for both personal and professional use. Advanced technologies like beamforming and MIMO improve signal strength and stability, reducing the likelihood of dropped connections and ensuring consistent performance. This reliability is particularly important for critical applications like telemedicine, remote work, and industrial automation.
Increased Capacity and Reduced Interference
Operating in higher frequency bands allows GHz wireless technology to accommodate more devices simultaneously without significant degradation in performance. This increased capacity is essential in environments with high device density, such as offices, stadiums, and smart cities. Additionally, the use of multiple channels and frequency bands helps minimize interference, ensuring smoother and more efficient communication.
Scalability and Flexibility
GHz wireless technology is highly scalable, capable of adapting to growing connectivity demands. As the number of connected devices continues to rise with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), GHz wireless networks can expand to support new applications and services. The flexibility of GHz bands also allows for the seamless integration of emerging technologies, paving the way for future innovations.
Energy Efficiency
Modern GHz wireless technologies are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Enhanced power management techniques reduce the energy consumption of devices, prolonging battery life and minimizing environmental impact. This is particularly beneficial for portable and battery-operated devices, where energy efficiency is paramount.
Applications of GHz Wireless Technology

Consumer Electronics
Wi-Fi Networks
Wi-Fi is perhaps the most ubiquitous application of GHz wireless technology. Operating primarily in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, Wi-Fi provides the backbone for home and office networks, enabling internet access, streaming services, and smart home functionalities. The introduction of Wi-Fi 6 and the upcoming Wi-Fi 7 standards further enhance speed, capacity, and efficiency, supporting a vast array of connected devices.
Bluetooth Devices
Bluetooth technology, which typically operates in the 2.4 GHz band, relies on GHz wireless communication for short-range connectivity between devices. From wireless headphones and keyboards to smartwatches and fitness trackers, Bluetooth facilitates seamless interactions and data exchange, enhancing user convenience and device interoperability.
Industrial and Commercial Use
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT ecosystem thrives on GHz wireless technology, connecting a multitude of devices ranging from sensors and actuators to smart appliances and industrial machinery. GHz wireless networks provide the necessary bandwidth and reliability to support real-time data transmission, enabling applications such as smart cities, automated manufacturing, and environmental monitoring.
Smart Manufacturing
In the realm of smart manufacturing, GHz wireless technology enables seamless communication between machinery, robots, and control systems. This connectivity enhances operational efficiency, facilitates predictive maintenance, and supports real-time monitoring and data analytics, driving the evolution towards Industry 4.0.
Healthcare
Telemedicine
GHz wireless technology plays a crucial role in telemedicine, enabling high-quality video consultations, remote patient monitoring, and real-time data transmission from medical devices. This enhances access to healthcare services, particularly in remote and underserved areas, and improves patient outcomes through timely and accurate information sharing.
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
Advanced GHz wireless systems support high-speed data transfer required for medical imaging and diagnostic equipment. This ensures that large datasets, such as MRI and CT scans, are transmitted swiftly and securely, facilitating prompt analysis and decision-making by healthcare professionals.
Entertainment and Media
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
The immersive experiences offered by VR and AR technologies are heavily reliant on GHz wireless communication. High data rates and low latency are essential for rendering real-time graphics and interactions, providing users with seamless and responsive virtual environments. The 60 GHz band, in particular, is ideal for wireless VR setups, delivering the necessary performance for high-definition, lag-free experiences.
Streaming Services
Streaming high-definition and ultra-high-definition (4K/8K) video content demands substantial bandwidth and reliable connectivity. GHz wireless technology, especially in the 5 GHz band, meets these requirements, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted streaming for consumers. This enhances the viewing experience and supports the growing demand for high-quality digital media.
Transportation
Connected Vehicles
In the automotive industry, GHz wireless technology facilitates the development of connected and autonomous vehicles. Real-time communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and control centers enables features such as collision avoidance, traffic management, and autonomous driving. This enhances road safety, improves traffic flow, and paves the way for the future of transportation.
Smart Infrastructure
Smart transportation infrastructure, including traffic lights, toll booths, and parking systems, relies on GHz wireless technology for efficient communication and data exchange. This integration improves the overall functionality and responsiveness of transportation systems, contributing to smarter and more sustainable urban mobility.
Future Trends in GHz Wireless Technology
5G and Beyond
The advent of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of GHz wireless communication. Operating across a broad spectrum of frequencies, including the sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave (mmWave) bands, 5G offers unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity. As the global rollout of 5G continues, it lays the foundation for innovations in IoT, smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and more. Looking ahead, research into 6G technology promises even greater advancements, with potential speeds reaching up to 1 terabit per second and enhanced capabilities for emerging applications.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize GHz wireless technology by optimizing network performance, enhancing security, and enabling intelligent resource management. AI-driven algorithms can predict and mitigate network congestion, automate maintenance, and personalize user experiences. This synergy between GHz wireless technology and AI/ML will lead to more adaptive, efficient, and resilient communication networks.
Advanced MIMO and Beamforming
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) and beamforming technologies are continually advancing, enhancing the capacity and coverage of GHz wireless networks. Massive MIMO, which utilizes a large number of antennas, increases data throughput and spectral efficiency. Beamforming, on the other hand, directs signal energy towards specific devices, improving signal strength and reducing interference. These technologies are critical for supporting the growing demand for high-speed and reliable wireless connections.
Expansion of the 60 GHz Band
The 60 GHz band, known for its ultra-high data rates and low latency, is poised for significant expansion. Applications in wireless VR/AR, high-definition video streaming, and ultra-fast data transfer are driving the adoption of this band. Innovations in antenna design, signal processing, and beamforming will enhance the practicality and performance of 60 GHz wireless systems, making them more accessible and versatile for various use cases.
Enhanced Security Measures
As wireless networks become more pervasive, ensuring their security is paramount. Future GHz wireless technologies will incorporate advanced encryption, authentication protocols, and intrusion detection systems to protect data integrity and privacy. Quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms may also be integrated to safeguard against emerging cyber threats, ensuring that wireless communication remains secure in an increasingly connected world.
Sustainable and Green Wireless Technology
Sustainability is becoming a key consideration in the development of GHz wireless technology. Innovations aimed at reducing energy consumption, utilizing eco-friendly materials, and minimizing the environmental impact of network infrastructure are gaining prominence. Energy-efficient protocols, renewable energy-powered base stations, and recyclable components are among the strategies being employed to create greener and more sustainable wireless networks.
Internet of Everything (IoE)
Building on the foundation of the Internet of Things (IoT), the Internet of Everything (IoE) envisions a world where not just devices, but people, processes, data, and things are interconnected. GHz wireless technology is integral to realizing this vision, providing the connectivity and bandwidth needed to support an expansive and diverse array of interconnected elements. This holistic integration will drive innovation across industries, fostering smarter environments and enhancing quality of life.
Practical Advice for Leveraging GHz Wireless Technology
For Consumers
- Optimize Your Home Wi-Fi Network:
- Use dual-band routers to take advantage of both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Position your router centrally to maximize coverage.
- Reduce interference by minimizing obstacles and avoiding overlapping channels.
- Upgrade to Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E:
- Invest in devices that support the latest Wi-Fi standards for enhanced speed, capacity, and security.
- Ensure your router is compatible with these standards to fully utilize their benefits.
- Secure Your Wireless Network:
- Use strong encryption (WPA3) to protect your network from unauthorized access.
- Regularly update your router’s firmware to address security vulnerabilities.
For Businesses
- Invest in Scalable Network Infrastructure:
- Deploy GHz wireless solutions that can scale with your business needs and support future growth.
- Utilize advanced technologies like MIMO and beamforming to enhance network performance.
- Leverage IoT for Operational Efficiency:
- Implement IoT devices and sensors to streamline operations, monitor assets, and gather valuable data.
- Ensure your wireless network can handle the increased connectivity demands of IoT deployments.
- Prioritize Network Security:
- Adopt comprehensive security measures, including encryption, authentication, and regular security audits.
- Educate employees on best practices for maintaining network security and preventing breaches.
For Developers and Technologists
- Stay Updated with Emerging Standards:
- Keep abreast of the latest advancements in wireless technology standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 7, 6G).
- Participate in industry forums and collaborate with peers to share knowledge and insights.
- Focus on Innovation and Integration:
- Explore novel applications of GHz wireless technology in areas like AR/VR, autonomous systems, and smart environments.
- Integrate AI and ML to optimize network performance and develop intelligent solutions.
- Address Environmental Sustainability:
- Develop energy-efficient wireless solutions that minimize power consumption and environmental impact.
- Explore sustainable materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes for wireless devices.
Relevant Statistics and Insights
- Global Wi-Fi Market: The global Wi-Fi market is projected to reach $56 billion by 2028, driven by the proliferation of smart devices and the expansion of wireless networks.
- 5G Adoption: As of 2024, over 1.5 billion 5G connections have been established worldwide, with significant growth expected in the coming years.
- IoT Growth: The number of IoT devices is expected to surpass 30 billion by 2025, highlighting the critical role of GHz wireless technology in supporting this expansion.
- Data Consumption: Average global mobile data consumption is projected to exceed 100 GB per user per month by 2025, underscoring the need for high-capacity GHz wireless networks.
- Bandwidth Requirements: Emerging applications like AR/VR and high-definition streaming require bandwidths in the range of several GHz to deliver seamless and immersive experiences.
Conclusion: Embracing the GHz Wireless Future
The rise of GHz wireless technology is reshaping the fabric of our connected world, offering unprecedented speeds, reliability, and capacity. From enhancing consumer experiences with faster internet and smarter devices to enabling transformative applications in industry, healthcare, and transportation, GHz wireless technology is at the forefront of the digital revolution. As we look to the future, ongoing advancements and innovative applications promise to unlock even greater potentials, driving us toward a more connected, efficient, and intelligent society.
Embracing GHz wireless technology requires a nuanced understanding of its benefits, applications, and emerging trends. Whether you’re a consumer seeking to optimize your home network, a business aiming to enhance operational efficiency, or a technologist pushing the boundaries of innovation, GHz wireless technology offers the tools and capabilities to thrive in an increasingly interconnected world. By staying informed and leveraging the power of GHz wireless technology, we can harness its full potential to create a smarter, faster, and more connected future.
FAQs, GHz Wireless Technology
1. What is GHz Wireless Technology?
Answer: GHz Wireless Technology refers to wireless communication systems that operate at specific frequencies measured in gigahertz (GHz). These frequencies are part of the electromagnetic spectrum and are commonly used for transmitting data in wireless networks, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
2. What is the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wireless frequencies?
Answer: The main difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz is the speed and range they offer. 2.4 GHz provides a wider range but lower speed, while 5 GHz offers faster speeds but a shorter range. Devices that support dual-band Wi-Fi can switch between these frequencies depending on network conditions.
3. Why is GHz important in wireless technology?
Answer: The GHz frequency determines the speed and bandwidth of wireless communications. Higher GHz frequencies (like 5 GHz) allow for faster data transmission, while lower frequencies (like 2.4 GHz) provide better coverage over longer distances and can penetrate obstacles like walls more effectively.
4. What GHz frequencies are used in Wi-Fi technology?
Answer: Wi-Fi technology primarily uses the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. More recent Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6 also utilize a 6 GHz band, providing even faster data transfer and less interference in crowded environments.
5. Is 5 GHz always better than 2.4 GHz?
Answer: Not necessarily. While 5 GHz provides faster data rates, it has a shorter range compared to 2.4 GHz and is less effective at penetrating walls and other obstacles. Depending on your location and network setup, 2.4 GHz may offer better performance in some cases.