Introduction
In recent years, the evolution of wireless technology has made remarkable strides, with 5G Wireless Technology at the forefront of this transformation. As the fifth generation of mobile networks, 5G promises not only to enhance connectivity but also to revolutionize industries, reshape economies, and change the way we interact with technology.
With its potential for lightning-fast data transfer speeds, low latency, and the ability to connect a multitude of devices, 5G has sparked excitement and anticipation worldwide. However, it also presents significant challenges and concerns that warrant discussion.
This article delves into the intricacies of 5G technology, exploring its benefits, challenges, and the profound impact it may have on society.
What is 5G Wireless Technology?

5G, or fifth-generation wireless technology, represents a significant leap forward from its predecessors—4G LTE and 3G. While 4G brought mobile internet access to the masses with decent speeds and improved connectivity, 5G aims to achieve even greater heights.
Key Features of 5G Technology
- Higher Speeds: 5G networks are designed to provide data speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G. This translates to download speeds exceeding 10 Gbps in optimal conditions.
- Low Latency: One of the defining features of 5G is its low latency, which can be as low as 1 millisecond. This rapid response time is crucial for applications requiring real-time feedback, such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgeries.
- Massive Connectivity: 5G is engineered to support a vast number of devices simultaneously. It can connect up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, facilitating the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Enhanced Capacity: 5G networks offer improved capacity to handle increased traffic and the surge of connected devices without compromising speed or performance.
How 5G Works
5G technology employs various techniques, including:
- Millimeter Waves: These high-frequency waves (above 24 GHz) can carry large amounts of data but have a shorter range. To maximize coverage, 5G networks will utilize a mix of frequencies, including sub-6 GHz.
- Small Cells: To overcome the limitations of millimeter waves, 5G networks deploy small cells—low-power base stations that help extend coverage and capacity in dense urban areas.
- Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output): This technology utilizes multiple antennas at the base station to send and receive more data simultaneously, enhancing network capacity and efficiency.
Benefits of 5G Wireless Technology

1. Enhanced Mobile Broadband
With significantly increased download and upload speeds, 5G offers an unparalleled mobile internet experience. Users can stream high-definition videos, engage in virtual reality (VR) gaming, and download large files within seconds. This enhancement is especially beneficial in areas with high user density, such as urban environments and events. To understand the technological foundations that enable these advancements, explore our comprehensive guide on 4G Wireless Technology Explained, which lays the groundwork for understanding how we transitioned from previous generations to the remarkable capabilities of 5G.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) Revolution
5G technology is set to accelerate the growth of IoT, enabling smart cities, connected vehicles, and smart homes. This enhanced connectivity facilitates real-time data exchange between devices, improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enhancing user experiences.
Example:
In smart cities, 5G can support applications such as traffic management systems that communicate in real time with vehicles and infrastructure, optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion.
3. Improved Healthcare Solutions
The healthcare industry stands to gain immensely from 5G technology. Low-latency connections enable telemedicine solutions, allowing healthcare professionals to conduct remote consultations and surgeries. Wearable devices can transmit health data instantaneously to healthcare providers, ensuring timely interventions.
Example:
Surgeons could perform remote operations using robotic instruments, guided by real-time video feeds, thanks to the minimal latency of 5G.
4. Industrial Automation
Manufacturers and industries are increasingly adopting smart factories powered by 5G. The technology facilitates seamless communication between machines, sensors, and human operators, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
Example:
In a 5G-enabled factory, robots can communicate with each other to coordinate tasks, enhancing production lines and reducing operational costs.
5. Economic Growth and Job Creation
The deployment of 5G technology is expected to drive economic growth by creating new jobs and opportunities across various sectors. According to a study by the GSMA, 5G is projected to contribute $2.2 trillion to the global economy by 2034, creating 22 million new jobs.
Challenges of 5G Wireless Technology
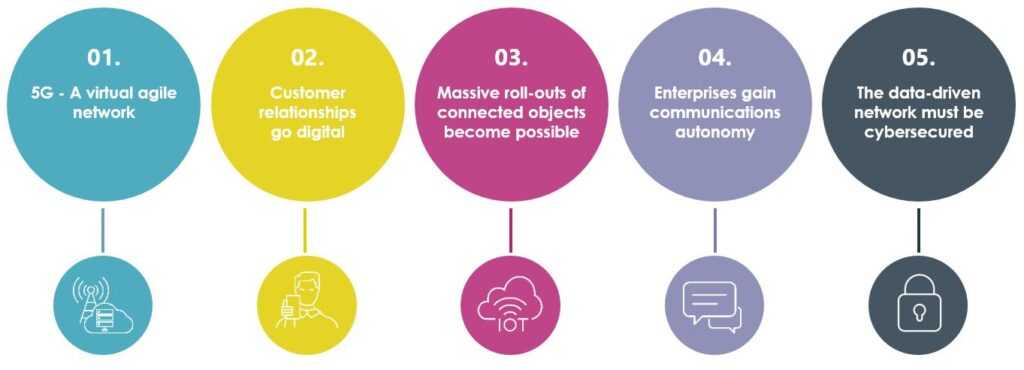
Despite its numerous advantages, 5G technology faces several challenges that could hinder its widespread adoption.
1. Infrastructure Investment
The rollout of 5G requires substantial investment in infrastructure, including the installation of new antennas, small cells, and fiber optic cables. This demand for investment can be a barrier for many regions, particularly in developing countries.
2. Spectrum Allocation
5G operates on various frequency bands, and the allocation of these frequencies is a complex issue involving governments and regulatory bodies. Ensuring adequate spectrum availability is critical for successful 5G deployment.
3. Security Concerns
The increased connectivity of devices poses significant security challenges. As more devices connect to the network, the potential attack surface expands, raising concerns about data privacy and cyber threats.
Example:
With the rise of smart homes, vulnerabilities in connected devices can be exploited, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive information.
4. Health Concerns
Despite extensive research indicating that 5G technology is safe, concerns persist regarding the potential health effects of prolonged exposure to radiofrequency radiation. Public perception and misinformation can delay the adoption of 5G technology in certain areas.
5. Limited Coverage
While 5G technology promises high-speed connectivity, its range is limited compared to previous generations. In rural or remote areas, achieving comprehensive coverage remains a challenge.
The Impact of 5G Wireless Technology
The impact of 5G Wireless Technology extends beyond individual users and industries. Its implications for society, the economy, and technology are profound.
1. Social Connectivity
5G technology can bridge the digital divide by providing high-speed internet access to underserved areas. This connectivity enables remote learning, telehealth services, and access to information, enhancing overall quality of life.
2. Economic Disruption
As industries adapt to 5G technology, traditional business models may be disrupted. Companies that embrace digital transformation will thrive, while those that resist change may struggle to compete.
3. Environmental Sustainability
5G has the potential to contribute to environmental sustainability by optimizing energy consumption and reducing waste. Smart grids and connected devices can help manage energy use more efficiently, leading to a reduced carbon footprint.
4. Innovation Catalyst
The capabilities of 5G technology serve as a catalyst for innovation across various sectors. From smart agriculture to immersive entertainment, the possibilities for new applications are virtually limitless.
Conclusion
In summary, 5G Wireless Technology is set to revolutionize connectivity, driving innovation and enhancing the quality of life for individuals and communities alike. While the benefits are substantial—ranging from enhanced mobile broadband to the proliferation of IoT applications—the challenges associated with deployment and adoption cannot be overlooked. As stakeholders from governments to private enterprises work to address these challenges, the future of 5G technology looks promising.
Embracing this transformative technology will be essential for unlocking its full potential and ensuring that its benefits are realized across society.
As we stand on the cusp of this new era of connectivity, the need for informed discussion, collaboration, and responsible implementation has never been more critical. The journey of 5G is just beginning, and its impact will continue to unfold in the years to come.
FAQs, 5G Wireless Technology
1. What is 5G wireless technology?
5G wireless technology is the fifth generation of mobile network technology, designed to provide faster data speeds, lower latency, and increased connectivity compared to previous generations (such as 4G). It aims to support a wide range of applications, including enhanced mobile broadband, IoT (Internet of Things), and critical communications.
2. How does 5G differ from 4G?
5G offers significant improvements over 4G in terms of speed, capacity, and latency. While 4G networks provide speeds of up to 1 Gbps, 5G can reach speeds of 10 Gbps or more. Additionally, 5G has lower latency (as low as 1 millisecond), which is crucial for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
3. What are the benefits of 5G technology?
5G technology provides several benefits, including:
Higher Speeds: Faster download and upload speeds for seamless streaming and downloading.
Lower Latency: Reduced delay for real-time applications, improving user experience in gaming and virtual reality.
Increased Capacity: Ability to connect more devices simultaneously, facilitating the growth of IoT and smart cities.
Enhanced Reliability: Improved network performance, making it suitable for critical applications.
4. What applications can 5G technology support?
5G technology can support a wide range of applications, such as:
Enhanced mobile broadband (e.g., high-definition video streaming)
Smart cities (e.g., connected infrastructure and traffic management)
Industrial automation (e.g., robotics and smart manufacturing)
Autonomous vehicles (e.g., vehicle-to-everything communication)
Telemedicine (e.g., remote surgeries and consultations)
5. Will 5G work with existing devices?
Most existing devices are not compatible with 5G networks, as they require specific hardware to utilize the new technology. However, many manufacturers are producing 5G-capable devices, including smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices, that will take full advantage of the new network.